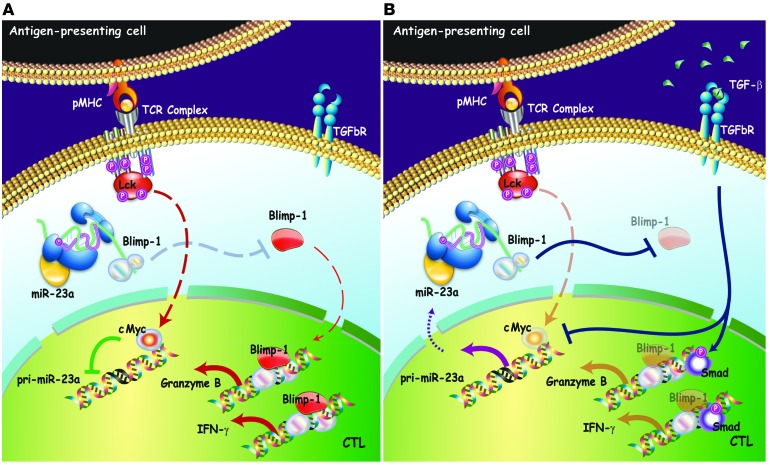
Figure 9. Model of CTL immune modulation by targeting miR-23a.
(A) Under immune-activating conditions, TCR signaling upregulates cMYC in CTLs. Transcriptional repression of pri-miR-23a by cMYC permits accumulation of BLIMP-1, resulting in increased expression of its cytotoxic target genes, granzyme B, and IFN-γ. (B) In the tumor microenvironment, TGF-β suppresses CTL activity via 2 mechanisms — SMAD-mediated transcriptional reprogramming and miRNA-mediated post-transcriptional control. In the former, TGF-β–induced SMADs are recruited to the Gzmb and Ifng gene regulatory regions to repress the transcription of these cytotoxic mediators directly. In the latter, TGF-β antagonizes cMYC activity, thereby derepressing pri-miR-23a transcription. Elevated miR-23a levels in CTLs downregulate BLIMP-1, and consequently its downstream cytotoxic effectors.