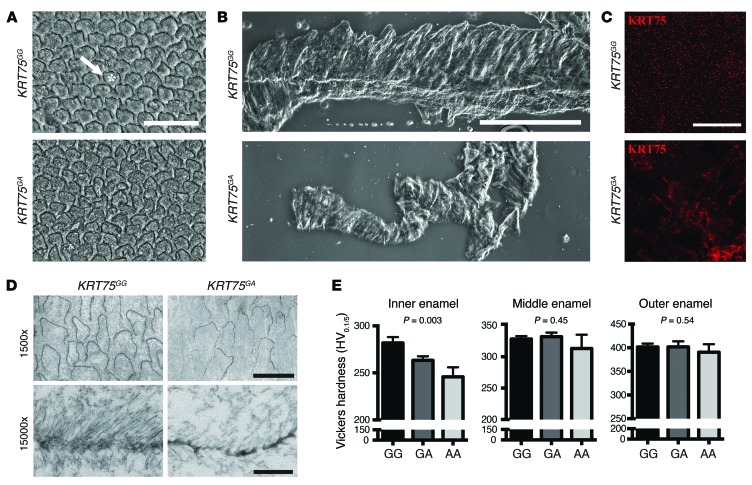
Figure 2. Effects of polymorphism in KRT75 on enamel and tufts structure and on enamel hardness.
(A) Scanning electron microscopy analysis of ground, polished, and etched human molars from patients with (KRT75GA) or without (KRT75GG) a missense A allele at rs2232387. Asterisk, rod; arrow, interrod. Scale bar: 20 μm. (B) Differential interference contrast imaging of tufts isolated from molars from individuals with KRT75GG or KRT75GA genotype. Scale bar: 500 μm. (C) Detection of KRT75 protein in tufts from individuals with KRT75GG or KRT75GA genotype. Scale bar: 20 μm. (D) Transmission electron microscopy of organic material isolated after demineralization of enamel from individuals with KRT75GG or KRT75GA genotype. Lower panels show high resolution images of enamel rod sheaths. Scale bars: 10 μm (upper panels); 500 nm (lower panels). (E) Vickers enamel hardness (adjusted for race) measured on molar sections from individuals with KRT75GG, KRT75GA, or KRT75GA genotype. n = 6 (3 of mixed European descent and 3 African-Americans) for each group.