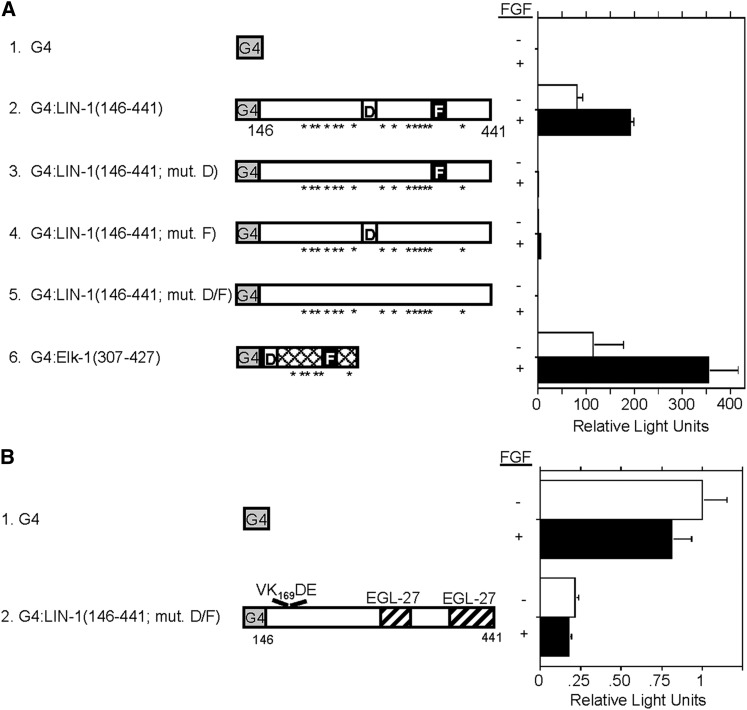
Figure 6.
The carboxy-terminus of LIN-1 contains an ERK-dependent transcriptional activation domain and an ERK-independent repression domain. MC3T3 murine fibroblast cells were transfected with the following: the pFR-LUC reporter plasmid that contains five tandem GAL4-binding sites upstream of a basal promoter that regulates expression of luciferase; an expression plasmid that encodes GAL4 DNA-binding domain (G4) alone or fused to the indicated fragment of LIN-1 or Elk-1; and a reporter plasmid that encodes β-galactosidase to measure transfection efficiency. Cells were untreated (−) or treated with basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) to activate ERK (+). (A) The schematics illustrate the ERK MAP kinase docking sites, the D-domain (D) and the FQFP motif (F). Asterisks indicate 15 S/TP motifs in LIN-1 that are potential ERK phosphorylation sites and 6 S/TP motifs in Elk-1 that are phosphorylated by ERK (Cruzalegui et al. 1999). Bars indicate luciferase activity divided by β-galactosidase activity. Values were normalized by setting the value for G4 alone in the absence of FGF to 1.0. Values represent the average and standard deviation of two to five independent transfections conducted in parallel. (B) The schematic of LIN-1 illustrates the VK169DE consensus SUMOylation motif (top) and two domains that are sufficient to bind EGL-27 (hatched).