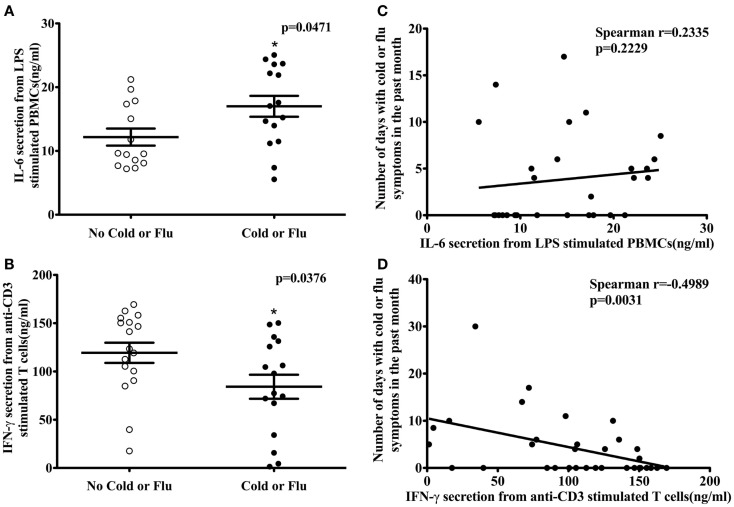
Figure 3.
LPS-stimulated IL-6 secretion from PBMCs, anti-CD3-stimulated IFN-γ secretion from T cells, and self-reported cold or flu status in human subjects. IL-6 secretion from LPS-stimulated PBMCs was significantly higher in subjects with self-reported cold or flu symptoms compared to subjects without cold or flu symptoms [(A); Mann–Whitney test, p = 0.0471]. IL-6 secretion was not correlated with number of days with cold or flu symptoms [(C); Spearman r = 0.2335, p = 0.2229]. IFN-γ secretion from anti-CD3-stimulated T cells in subjects with cold or flu symptoms was significantly lower compared to subjects without cold or flu symptoms [(B); unpaired t-test, p = 0.0376]. T-cell IFN-γ secretion was inversely associated with total number of days with self-reported cold or flu symptoms [(D); Spearman r = −0.4989, p = 0.0031]. Asterisk indicates a significant difference from no cold or flu group (p < 0.05).