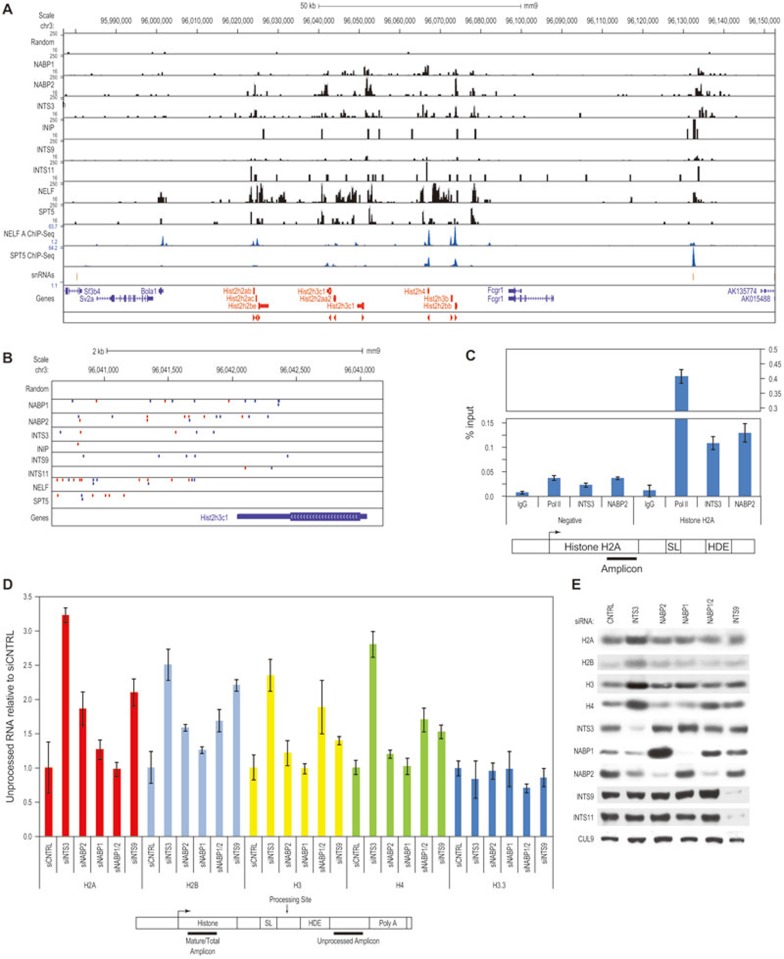
Figure 3.
The Integrator complex regulates replication-dependent histone genes. (A) Integrator, NELF, and DSIF bind replication-dependent histone genes. HIT-Seq data for a 200 kb section of mouse chromosome 3, containing histone cluster 2. The HIT-Seq data for each construct is presented as CPKM. The NELF dataset is a composite of all NELF subunits analyzed by HIT-Seq, and the NELF and SPT5 ChIP-Seq datasets are previously published31. The orientation of histone gene transcription is shown at the bottom. (B) Integrator, NELF, and DSIF bind the 3′ region of replication-dependent histone genes. A higher magnification of individual virus integrations at the Hist2h3c1 gene from the chromosome 11 locus is shown to illustrate binding in the 3′ region. Blue and red marks indicate the orientation of each virus integration. (C) ChIP was performed from T98G cells using the indicated antibodies and was analyzed by qPCR for the indicated amplicon at the histone H2A locus. A negative control primer in an intergenic region was also analyzed. Error bars show the SD of three PCR reactions. (D) Random primed cDNAs from HeLa cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs were analyzed by qPCR for unprocessed and total (mature) histone transcripts as indicated. For histone H3.3, which is not processed, qPCR was performed for the 3′UTR and coding region. The results for each histone are presented relative to the control sample. The data is presented as mean ± SD. The general location of each primer is indicated below the graph. (E) Western blotting was performed with lysates from HeLa cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs.