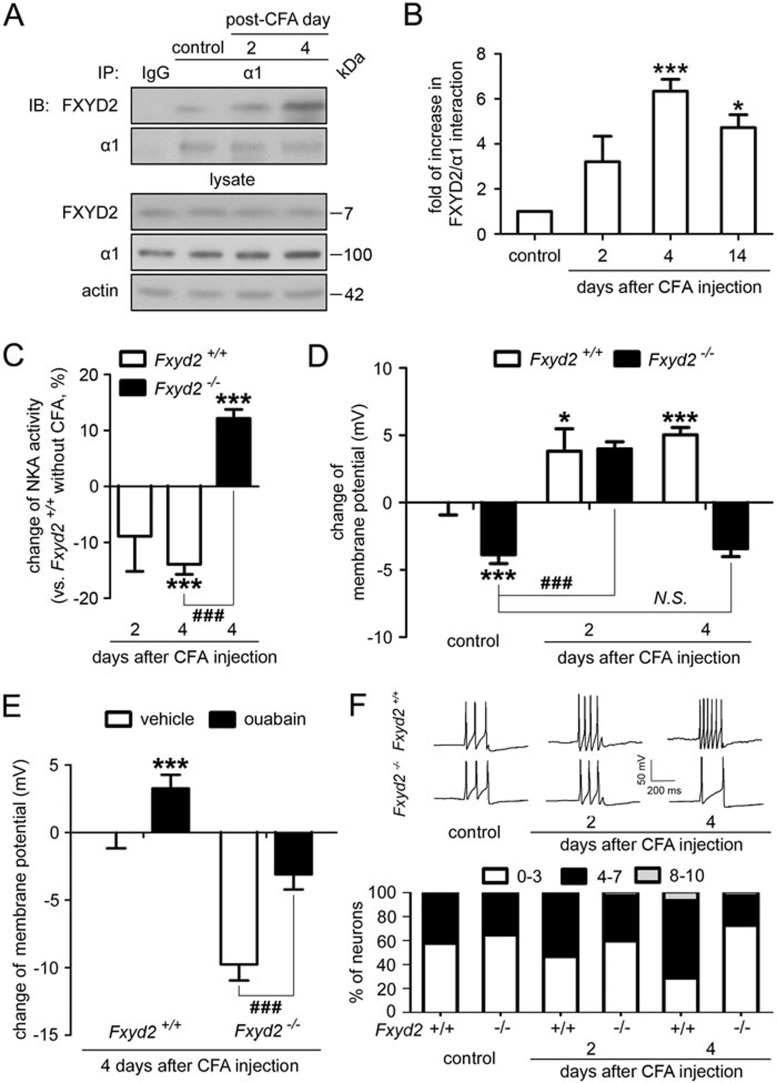
Figure 5.
FXYD2 is required for maintaining the inflammation-induced membrane depolarization and excitability. (A) Co-IP showed that the interaction between FXYD2 and the α1 subunit of NKA increased gradually after peripheral inflammation and peaked on day 4 after injection. (B) Quantitation showed that the interaction between FXYD2 and the α1 subunit of NKA increased gradually and peaked on day 4 (n = 4, ***P < 0.001). The increased interaction lasted for 14 days, although the average interaction level on day 14 was lower than that on day 4 (n = 3, *P < 0.05). (C) The NKA activity gradually decreased in the DRGs of Fxyd2+/+ mice treated with CFA for 2 and 4 days (n = 3 for CFA day 2 and n = 6 for CFA day 4, ***P < 0.001 vs Fxyd2+/+mice without CFA treatment). However, 4 days after CFA treatment, the NKA activity in the DRGs of Fxyd2−/− mice was not significantly different from that in the DRGs of Fxyd2+/+ mice without CFA treatment. The reduction of NKA activity in the DRGs of Fxyd2+/+ mice was reversed by deletion of Fxyd2 (n = 5, ***P < 0.001 vs Fxyd2+/+mice without CFA treatment and ###P < 0.001 vs indicated). (D) Whole-cell patch clamp recording at current-clamp mode showed that the membrane potential of small DRG neurons cultured from Fxyd2+/+mice was depolarized after CFA injection (n = 52 for control, n = 55 for CFA 2 days and n = 65 for CFA 4 days, *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001 vs Fxyd2+/+mice without CFA treatment). The membrane potential of small DRG neurons cultured from Fxyd2−/− mice was also depolarized 2 days after CFA injection (n = 54 for control and n = 49 for CFA 2 days, ###P < 0.001 vs indicated). However, 4 days after CFA injection, the depolarized membrane potential was reversed in small DRG neurons of Fxyd2−/− mice (n = 67 for CFA 4 days; N.S., non-significant difference). The data were shown as the change of membrane potential and statistic analysis was performed for the membrane potential between the indicated groups. (E) Bath-applied ouabain (1 mM) depolarized the membrane potential of small DRG neurons of both Fxyd2+/+ and Fxyd2−/− mice 4 days after CFA injection (n = 13 for Fxyd2+/+ mice and n = 14 for Fxyd2−/− mice, ***P < 0.001 vs Fxyd2+/+ mice 4 days after CFA injection, before ouabain treatment and ###P < 0.001 vs indicated). The data were shown as the change of membrane potential and statistic analysis was performed for the membrane potential between the indicated groups. (F) The current (70 pA, 200 ms) was injected to induce sustained firing of IB4-positive small DRG neurons. Representative traces showed that the firing frequency of AP was increased in IB4-positive small DRG neurons from Fxyd2+/+ mice 2 and 4 days after CFA injection, whereas the firing rate of AP was decreased in the neurons from Fxyd2−/− mice 4 days after CFA injection. The number of IB4-positive small DRG neurons with a low firing frequency of AP (0-3 APs per stimulation) was decreased gradually in Fxyd2+/+ mice after CFA injection, but was increased in Fxyd2−/− mice 4 days after CFA injection (n = 42 for control, n = 39 for CFA 2 days and n = 50 for CFA 4 days in Fxyd2+/+ mice; n = 59 for control, n = 46 for CFA 2 days and n = 57 for CFA 4 days in Fxyd2−/− mice).