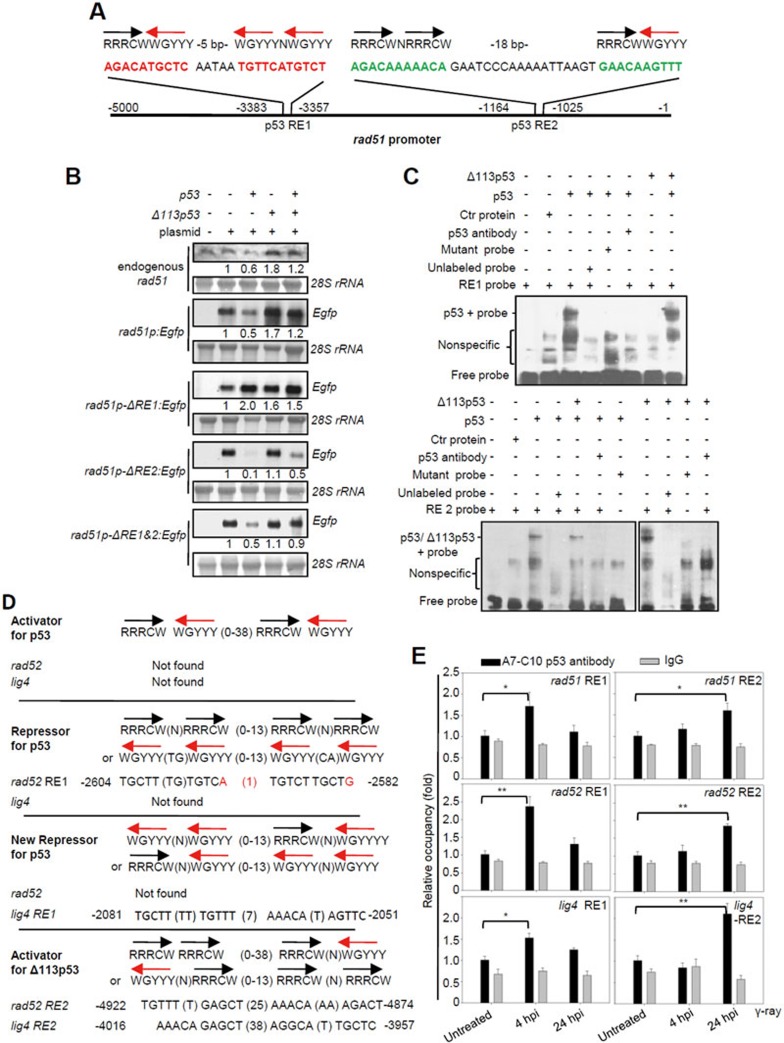
Figure 7.
Δ113p53 upregulates the expression of rad51, rad52 and lig4 by directly binding to a new type of p53 RE in their promoter regions. (A) The rad51 promoter. The black and red arrows correspond to the orientations of the quarter sites. R = A or G, W = A or T, Y = C or T. The positions of two p53 REs in the rad51 promoter are indicated. (B) Northern blot analysis of the transcription levels of endogenous rad51 and Egfp in p53M214K mutant embryos injected with rad51p:Egfp, rad51p-ΔRE1:Egfp (with a 26-bp deletion of RE1), rad51p-ΔRE2:Egfp (with a 39-bp deletion of RE2) and rad51p-ΔRE1+2:Egfp (with double deletions in RE1 and RE2) plasmids, or co-injected with these plasmids and p53, Δ113p53 or p53-plus-Δ113p53 mRNAs, as indicated. 28S rRNA was used as the loading control. The numbers between the panels are the relative gene expression levels normalized against 28S rRNA in each experiment. (C) EMSA was performed to detect p53 and Δ113p53 interactions with RE1 and RE2 in the rad51 promoter. The 26-bp DNA fragments of RE1 and an RE1 mutant with 6 bp mutated (AGAAATACAC AATAA TTTTCATTTAT; mutations are underlined), and 39-bp DNA fragments of RE2 and an RE2 mutant with 6 bp mutated (ATATAAAAATA GAATCCCAAAAATTAAGT GAAAAATTAT; mutations are underlined) of the rad51 promoter were labeled with biotin to form probes. Nuclear proteins were extracted from zebrafish p53M214K mutant embryos injected with different mRNAs as indicated. Labeled probes were incubated with different protein extracts, with unlabeled probes and zebrafish A7-C10 antibody, as indicated. (D) p53 and Δ113p53 REs in rad52 and lig4 promoters compared to other p53 REs. Mismatch nucleotides are labeled red. The positions of p53 REs in the respective promoters are indicated. (E) ChIP of RE1 and RE2 in rad51, rad52 and lig4 promoters in the irradiated embryos at 4 and 24 hpi. WT embryos were treated with γ-irradiation and sampled at 4 and 24 hpi, respectively. The A7-C10 p53 antibody was used to co-immunoprecipitate the protein-DNA complex, while IgG was used as a non-specific binding control. Specific primer pairs were designed to amplify the corresponding REs. DNA was normalized with a pair of negative control primers for β-actin exon. The results are presented as the relative occupancies of different REs. Statistics were obtained from three repeat experiments.