Figure 5.
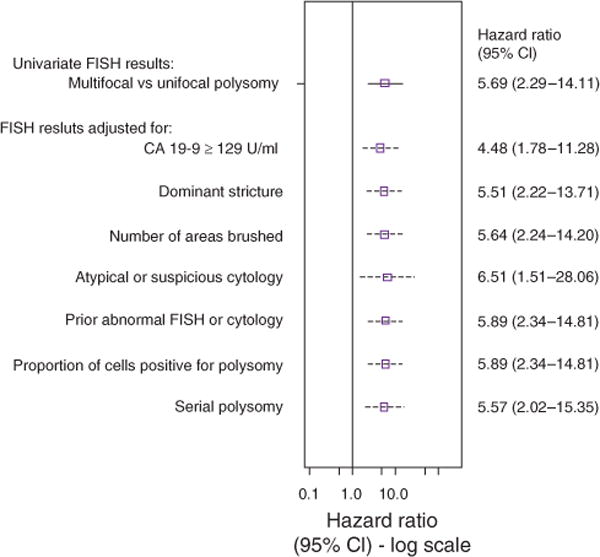
Forest plot illustrating the association of multifocal polysomy (compared with those with unifocal polysomy) with the probability of being diagnosed with cholangiocarcinoma after adjusting for other potential risk factors. The figure shows the point estimate (hazard ratio) and 95% confidence interval (CI) of MFP (unadjusted and adjusted for each individual covariate). The cytology adjustment includes two variables representing suspicious cytology vs. negative and atypical cytology vs. negative. A prior history of an abnormal FISH result or cytology included trisomy/tetrasomy or unifocal polysomy (among multifocal patients) and suspicious or atypical cytology results. CA 19-9, carbohydrate antigen 19-9; FISH, fluorescence in situ hybridization.
