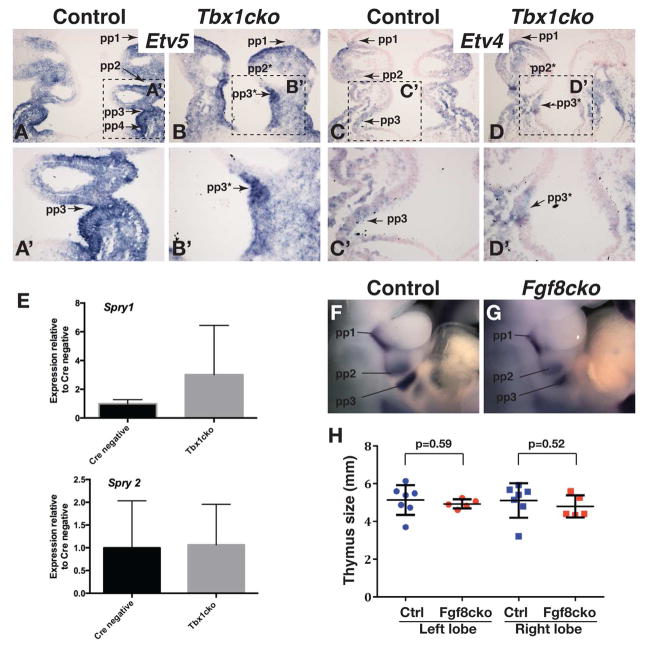
Figure 3. Normal levels of FGF signaling is maintained in Tbx1cko embryos.
A–D) The expression of two FGF signaling reporter genes, Etv5 (A,B) and Etv4 (C,D) in frontal sections through E9.5 pharyngeal apparatus are compared between control (A,C) and mutant (B,D) embryos. Pharyngeal pouches (pp1–pp4) and presumptive pouches (pp2*, pp3*) are indicated.
A′–D′) Magnified views of the areas indicated in panels A–D. Note the equivalent levels of gene expression in evaginating and presumptive 3rd pouches of control and mutant embryos.
E) Relative qRT-PCR quantification of FGF-regulated transcripts in the E9.5 pharyngeal region.
F,G) Pax1 in situ hybridization to visualize pharyngeal pouches in control (F) and Fgf8cko (G) embryos at E10.5. Note that of all pharyngeal pouches are present in the mutant.
H) Estimated sizes of thymus lobes at E17.5 as measured by thymus circumference from wholemount pictures. Note the absence of any significant thymus hypoplasia in Fgf8cko embryos.