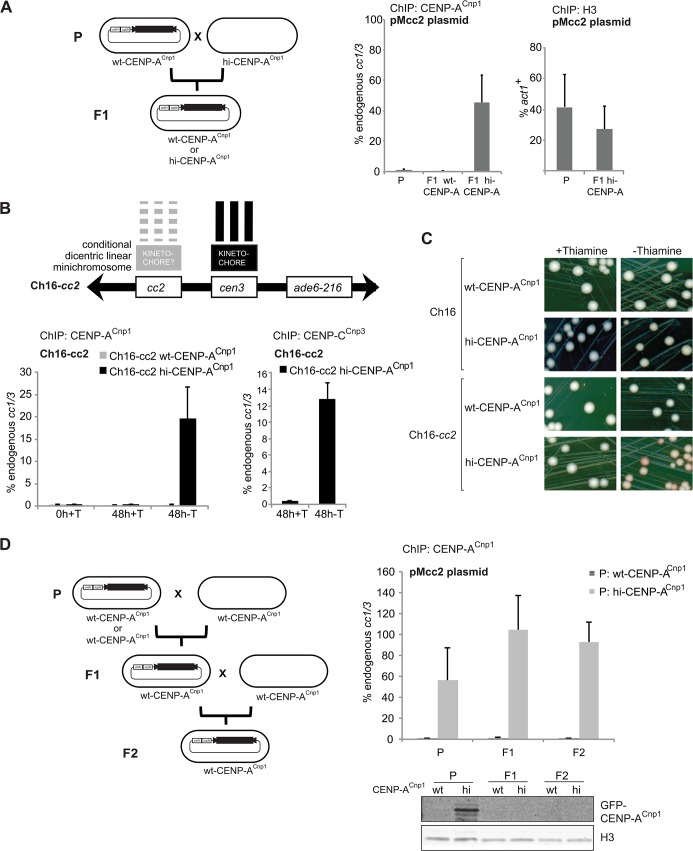
Fig 2. CENP-ACnp1 chromatin behaves as an epigenetic mark.
(A) A wild-type strain (parental: P; wt-CENP-ACnp1) was transformed with the pMcc2 plasmid and then crossed to a strain overexpressing CENP-ACnp1 (hi-CENP-ACnp1). From the first generation (F1) cells containing pMcc2 and expressing wild-type level or overexpressing CENP-ACnp1 were selected and analysed by ChIP for CENP-ACnp1 and H3 levels on the pMcc2 plasmid (P: n = 2, F1: n = 4) (B) cc2 was integrated on the arm of Ch16, that contains cen3, creating Ch16-cc2. Ch16-cc2 was crossed into a strain containing nmt41-GFP-CENP-ACnp1. In presence of thiamine (0h+T) GFP-CENP-ACnp1 is repressed. The same cells were diluted in medium containing thiamine (48+T; GFP-CENP-ACnp1 repressed) or without thiamine (48h-T; GFP-CENP-ACnp1 expressed) for 48h. ChIP was performed for CENP-ACnp1 and CENP-CCnp3 levels. (C) Colony colour sectoring assay for cells containing minichromosome Ch16 or Ch16-cc2. Red sectors indicate loss of minichromosomes. (D) A wild-type strain (wt-CENP-ACnp1) or a strain overexpressing CENP-ACnp1 (hi-CENP-ACnp1) were transformed with the pMcc2 plasmid (parental: P) and then crossed to a wt-CENP-ACnp1 strain. From the first generation (F1), wt-CENP-ACnp1 strains containing pMcc2 were selected and subsequently crossed to wt-CENP-ACnp1 strain. Progeny resulting from this second cross are referred to as second generation (F2). ChIP analysis for CENP-ACnp1 levels on the pMcc2 plasmid in the different generations relative to cc1/3; region M analysed by qPCR (P: n = 2, F1: n = 4, F2: n = 8).