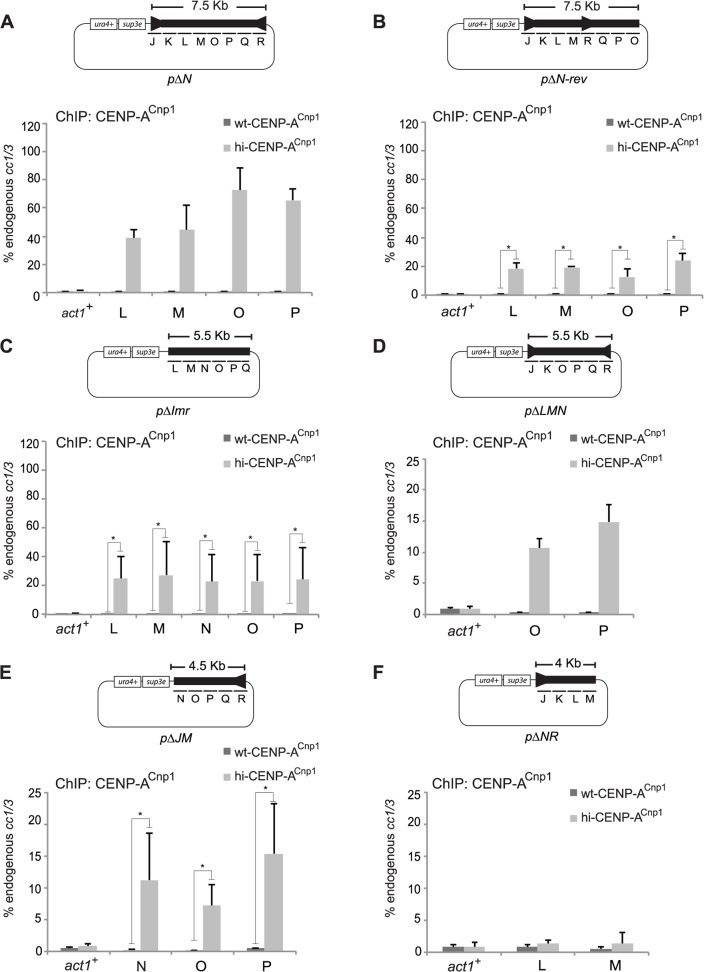
Fig 3. Centromeric DNA sequence affects CENP-ACnp1 chromatin establishment.
Plasmids containing fragments of cc2 DNA were transformed into wild-type (wt-CENP-ACnp1) or cells expressing high levels of CENP-ACnp1 (hi-CENP-ACnp1). Plasmids contained: (A) Deletion of central 1 kb (N) from cc2, (B) Left half of cc2, (J to M: 4 kb) plus region O to R (3.5 kb) in inverted orientation (region N absent), (C) imr2 regions (J and R) deleted along with 1 kb of cc2 (K), leaving LMNOPQ, (D) Region L to N deleted, leaving JKOPQR. (E) Deletion of J to M, leaving N to R, (F) Deletion from N to R, leaving J to M. The enrichment of CENP-ACnp1 on the plasmids was analysed by ChIP and calculated relative to the endogenous cc1/3 (n = 3). In (B), (C) and (E) p-value was calculated. Asterisks indicate p <0.05.