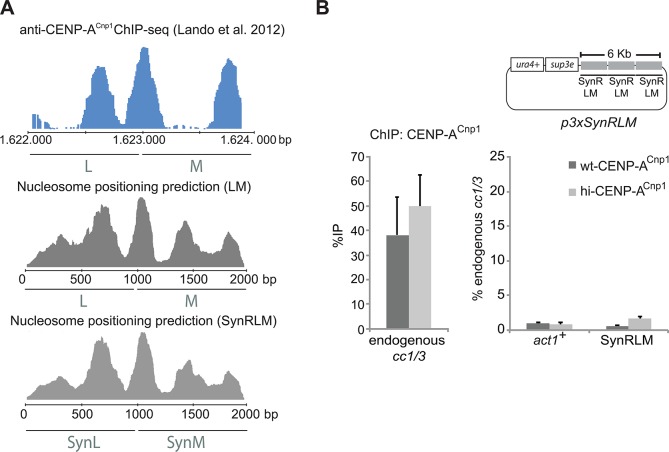
Fig 6. Genetic information contained within DNA sequence is required for centromeric chromatin establishment.
(A) Comparison between ChIP-seq data for CENP-ACnp1([49]; blue) and nucleosome positioning prediction (algorithm developed by [55]; in grey) for the LM region of cc2 or a mutagenised synthetic version of LM (SynRLM). The algorithm predicts nucleosome peaks within the central domain that match those mapped in vivo by ChIP-seq. SynRLM was designed by randomising the LM sequence in a 5 bp window and taking into consideration both periodicity of nucleosome positions and AT/GC content distribution of the original LM sequence. (B) ChIP analysis of CENP-ACnp1 levels of wild-type (wt-CENP-ACnp1) and cells overexpressing CENP-ACnp1 (hi-CENP-ACnp1) transformed with a plasmid containing three tandem repeats of SynRLM (p3xSynRLM). CENP-ACnp1 levels are shown relative to cc1/3 (n = 3).