Figure 1. Structure of Efr3-N.
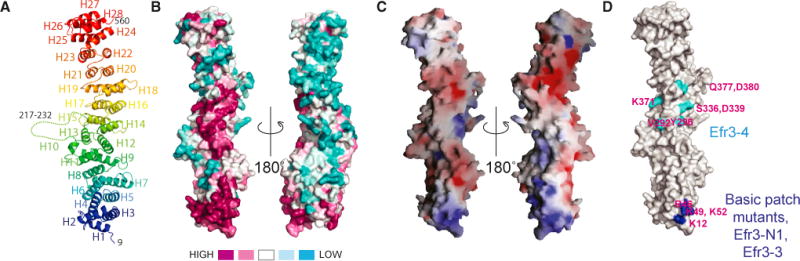
(A) Ribbons diagram, colored blue to red from N terminus to C terminus.
(B) Conservation in Efr3-N. Orientation at left is as in (A). Surfaces around the N terminus of Efr3-N and in the middle of the rod are highly conserved.
(C) Electrostatic potential. The conserved surface at the N terminus is basic.
(D) Location of mutations mapped onto structure. Residues H67 and R69, which are mutated in Efr3-3 and Efr3-N2, are in the conserved basic patch, but not visible here. Recombinant Efr3-3 is well folded as assessed by CD (Figure S2), but Efr3-4 aggregates in vitro.
