Figure 2.
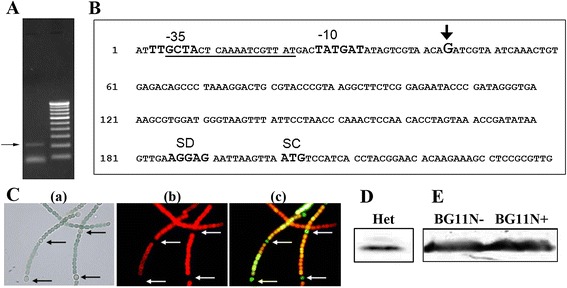
RACE analysis and expression of the alr4641 promoter ( P alr4641 )- gfp gene fusion. (A) RACE was performed with RNA isolated from Anabaena cells treated with H2O2 (1 mM) for 1 h using primers described in the Methods section. The ~200-bp DNA fragment is shown by an arrow. (B) Sequence analysis of the RACE product. The transcriptional start site is indicated by +1 in the figure. The nucleotide sequence corresponding to the −10 and −35 region of the alr4641 promoter, the ribosome binding site (SD) and the translational start codon (SC) are denoted while the FurA-binding sequence is underlined. (C) Bright field and fluorescence micrographs (1500X). An4641prom cells, were grown in medium lacking combined nitrogen for several generations and visualized under a fluorescence microscope; (a) bright field image, (b) fluorescence micrograph of cells using Hg-Arc lamp (excitation BP, 546–612 nm and emission LP, 515 nm) and (c) fluorescence micrograph (excitation BP, 450–490 nm and emission LP, 515 nm). Heterocysts are depicted by arrows. (D) Total protein from heterocysts (20 μg) was resolved by SDS-PAGE and probed with the Alr4641 antiserum. (E) Detection of the Alr4641 protein. The wild-type Anabaena PCC7120 cells were grown in BG-11 medium without (BG11N-) or with combined nitrogen (BG11N+). Protein extracts (60 μg per lane) were resolved by SDS-PAGE (10% gel), and immunodetected with the Alr4641 antiserum on Western blots. The 23 kD Alr4641 protein is depicted by an arrow.
