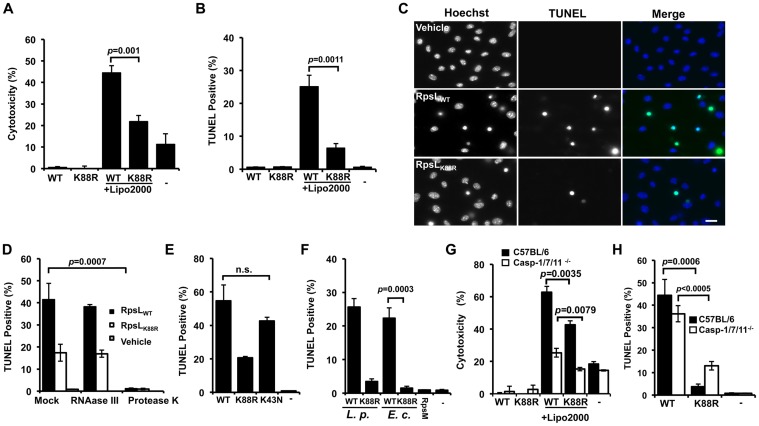
Fig 4. RpsL induces cell death in macrophage.
A–C. Induction of cell death by RpsL. BMDMs from A/J mice were transfected with 10 μg purified RpsL or RpsLK88R that had been washed with 60% isopropanol. 6 hrs posttransfection, samples were processed for measuring the level of LDH (A) or for TUNEL staining (B). Samples received the same amount of protein without the transfection reagent or treated with the transfection reagent only were set as controls. C. Representative images of the TUNEL staining of samples receiving RpsL or RpsLK88R. Note that adding the protein to the cell culture without the transfection reagent did not cause detectable cell death. Bar 10 μm. D. Protein but not dsRNA is responsible for the cell death. RNAase III or protease K was added to protein solution prior to transfection and samples were processed for TUNEL staining. E–F. Cell death induction by proteins relevant to RpsL. Macrophages transfected with RpsL, RpsLK88R, RpsLK43N, RpsM or RpsL from E. coli were processed for TUNEL staining. G–H. Macrophages from mice lacking caspases-1/7/11 are susceptible to cell death induced by RpsL. Macrophages prepared from the knockout or its parent mice were transfected with RpsL or RpsLK88R and samples were processed for LDH release measurement (G) or for TUNEL staining (H). In all experiments, each treatment was performed in triplicate and the quantitative results were obtained from scoring at least 500 cells from each sample. Similar results were obtained from at least three independent experiments.-, transfection reagent only.