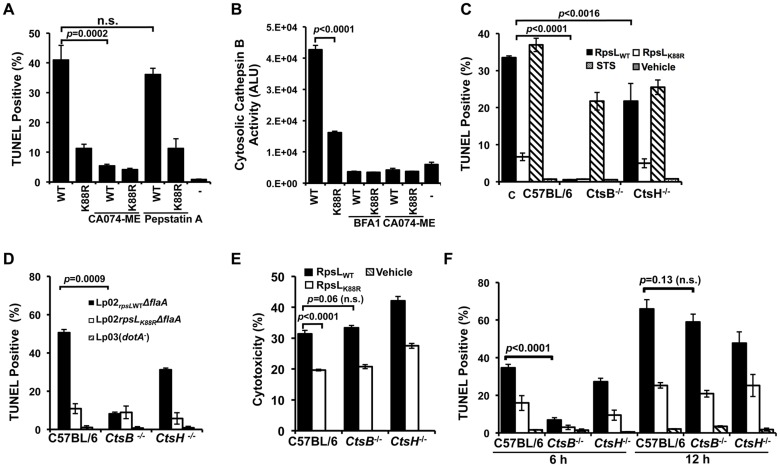
Fig 6. Cathepsin B is required for efficient RpsL-induced cell death in macrophages.
A. Inhibition of CtsB activity alleviated RpsL-induced macrophage death. BMDMs from A/J mice were treated with 25-μM CA-074ME (against CtsB), 25-μM pepstatin A (against CtsD) or the solvent DMSO for 1.5 hrs before protein transfection. Cells were then processed for TUNEL staining. B. RpsL induced cytosolic release of cathepsin B. 1x105 BMDMs in 96-well plates were transfected with the proteins for 8 hrs, and the cytosolic cathepsin activity was determined with the substrate zRR-AMC by measuring free AMC with a TECAN plate reader. C. Cathepsin B is required for RpsL-induced cell death at 6 hrs post protein transfection. BMDMs prepared from ctsB -/-, ctsH -/- or C57B/6 mice were transfected with RpsL or RpsLK88R for 6 hrs, and the cell death was evaluated by TUNEL staining. Samples treated with staurosporine were established as positive controls. D. Cell death induced by L. pneumophila expressing wild type RpsL required CtsB. BMDMs from the indicated mice were infected with relevant bacterial strains for 12 hrs at an MOI of 5 and cell death status of infected cells was determined by TUNEL staining. In both C and D, each treatment was performed in triplicate and TUNEL signals were assessed from at least 500 cells from each sample. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. E. RpsL caused plasma membrane damage in BMDMs from ctsB -/- mice. Macrophages from indicated mouse lines were transfected with RpsL or its K88R mutant for 6 hrs and the LDH release were then determined. Note the similar LDH release caused by RpsL among BMDMs from these mouse lines. F. BMDMs prepared from ctsB -/-, ctsH -/- or C57B/6 mice transfected with RpsL or RpsLK88R were fixed at 6 and 12 hrs post transfection, and the cell death was evaluated by TUNEL staining.-, transfection reagent only.