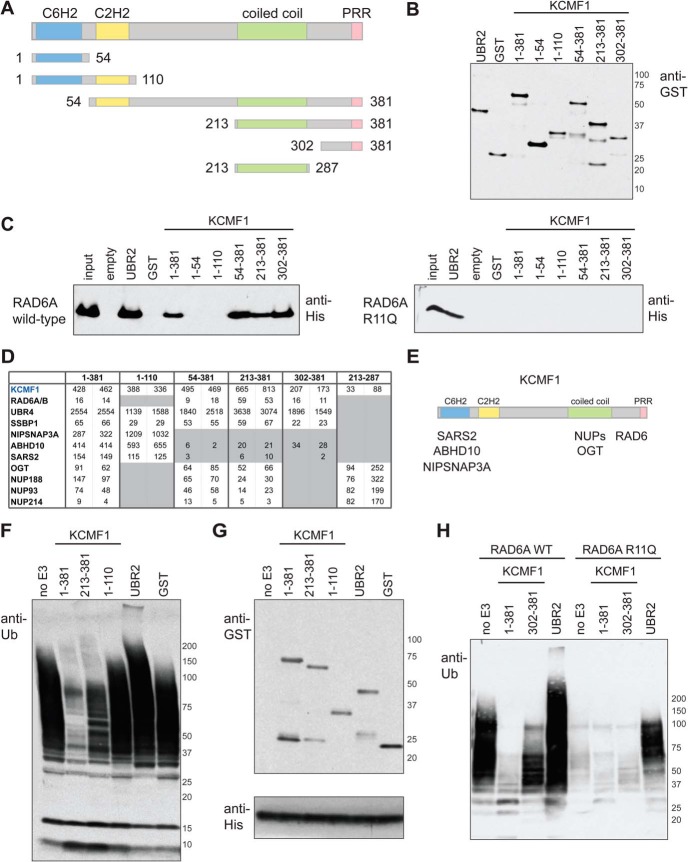
Fig. 1.
In vitro and in vivo interaction mapping of KCMF1. A, KCMF1 domain structure map, and deletion mutants used here for in vitro and in vivo binding assays. Amino acid residues assigned to each domain based on the Jpred3 secondary structure prediction program (49). PRR, proline-rich region. B, Recombinant GST alone, GST-UBR2 (BRR + RING domain fragment) and GST-tagged KCMF1 proteins (as indicated) were expressed in E. coli, purified, subjected to SDS-PAGE and analyzed via anti-GST Western blotting. C, In vitro RAD6A binding assay. Recombinant GST-KCMF1 (full-length and truncation mutants, as indicated), GST-UBR2 (BRR+RING domain) and GST alone were incubated with recombinant full-length His-RAD6A for 1h at 4 °C, followed by extensive washing. Proteins were eluted with Laemmli buffer, resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting with an antibody directed against 6xHis; (left) wild type RAD6A, (right) RAD6A R11Q mutant. D, In vivo KCMF1 interaction mapping. Flag-tagged full-length KCMF1 and truncation mutants were expressed in 293 T-REx cells and subjected to AP-MS. Two cell pools were generated independently. For each pool, two technical runs were conducted, and maximum spectral counts for each protein identification are indicated. All proteins highlighted here were detected with a >95% iProphet confidence level and SAINT score >0.95. Spectral count values highlighted in gray are ≤ 10% of those observed for full length (1–381) KCMF1. E, Binding regions for the indicated KCMF1 interactors, as determined by AP-MS. F, Autoubiquitylation reactions, performed with recombinant human E1 (90 nm), ubiquitin (5 ug) and His-RAD6A (3 μm) alone, or in the presence of equimolar amounts of GST alone, GST-UBR2 (BRR+RING), or GST-tagged KCMF1 protein fragments (as indicated), for 3 h at 30 °C. Reactions were subjected to SDS-PAGE and anti-ubiquitin Western blotting. G,, anti-GST (top panel) and anti-His (bottom panel) Western blotting of the autoubiquitylation reactions shown in F. H, Autoubiquitylation assays as in F, conducted with wild type and R11Q RAD6A proteins.