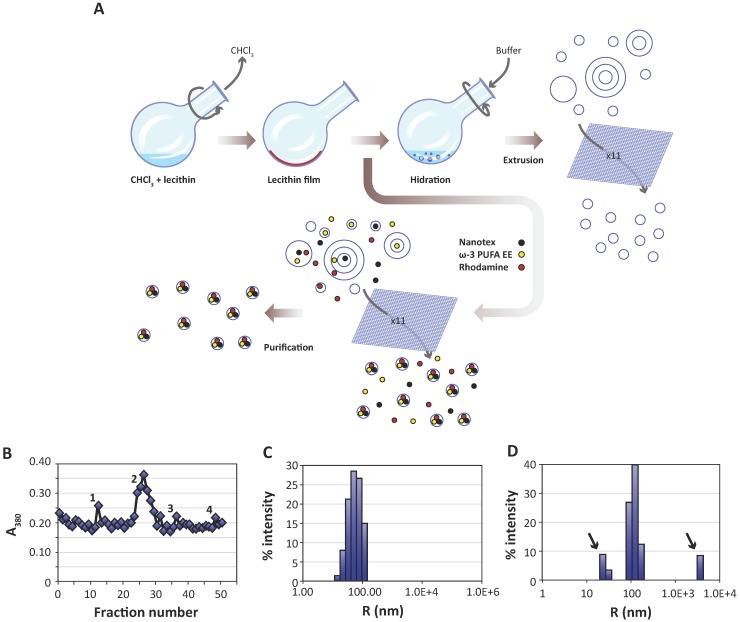
Figure 1.
Preparation and characterization of liposomes. A:Liposomes are prepared from egg yolk lecithin, containing or not ω-3 PUFA-EE, Nanotex or Rhodamine-100 by the film hydration method 39. A solution of chloroform and lecithin is rotated under vacuum to remove chloroform, depositing a thin lecithin film covering the round bottom flask. Hydration of this film with aqueous buffer results liposomes of heterogeneous sizes and different numbers of layers. Nanotex (black circles), ω-3 PUFA-EE (yellow circles) or Rhodamine-100 (red circles) may be added to the buffer, resulting in their intraluminal encapsulation. Some residual Nanotex, ω-3 PUFA-EE or Rhodamine-100 may remain in the extraliposomal space. Repeated extrusions (x11) result in crude homogeneous suspensions of liposomes loaded or not with added components in their lumen, but present also in the extraliposomal space. These may be removed later after a purification process, normally based in size exclusion chromatography (Sephadex G50) or centrifugal ultrafiltration through filters of controlled pore size. B: Absorption (turbidity) peaks at 380 nm from the column fractions loaded with a sample of liposomes with Nanotex and ω-3 PUFA-EE. Note that the elution profile presents an initial peak 1 corresponding to large Nanotex particle aggregates not encapsulated in the liposomes, followed by the most prominent peak 2 derived from liposomes containing PUFA-EE goticules and Nanotex, and extraliposomal free Nanotex particles (peak 3) or PUFA-EE goticules (peak 4). Representative DLS of a suspension of empty liposomes (C) and a suspension of liposomes loaded with ω-3 PUFA-EE (D). Black arrows indicate the size of smaller or larger aggregates of free ω-3 PUFA-EE.