Figure 1.
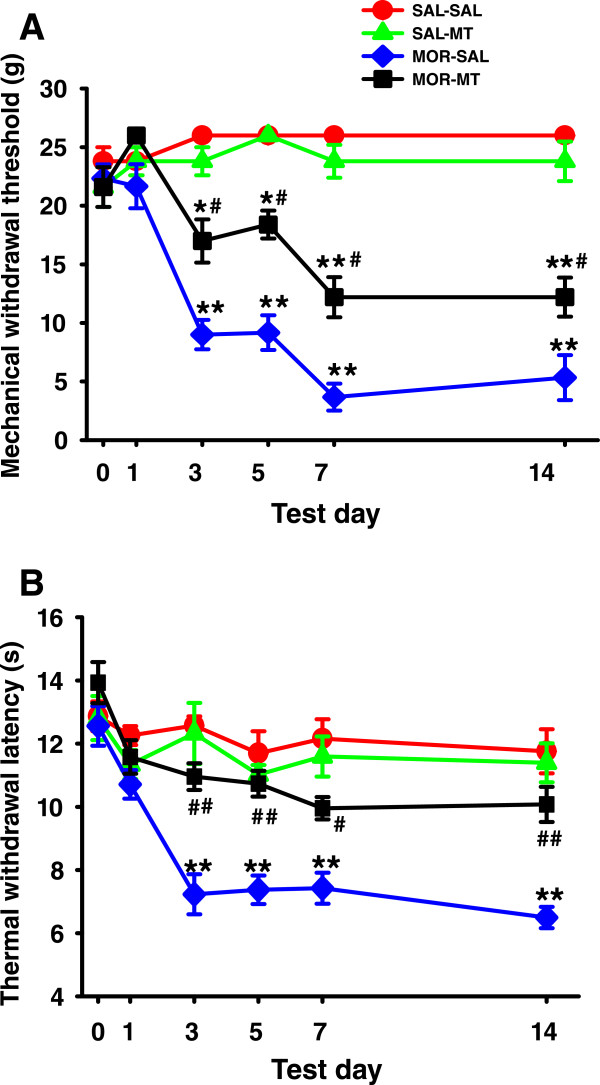
Melatonin attenuated morphine-induced mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia. A: Hindpaw withdrawal threshold to mechanical stimulation. B: Hindpaw withdrawal latency to thermal stimulation. Mechanical withdrawal threshold and thermal withdrawal latency were both gradually decreased and shortened, respectively, in rats that received morphine (10 mg/kg, s.c.) alone from day 3 to 14. Co-administration of morphine with melatonin(10 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly prevented the decreased withdrawal threshold and latency from day 3 to day 14. Six rats were included in each group. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, compared with SAL-SAL; # P <0.05 and ## P < 0.01, compared with MOR-SAL. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.
