Figure 2.
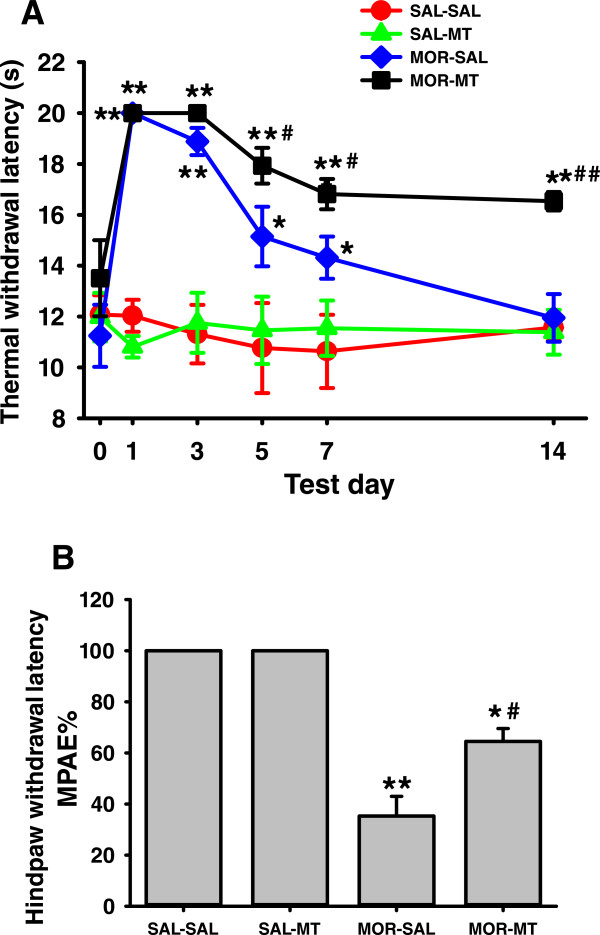
Effect of melatonin on the morphine tolerance. The development of the tolerance to morphine’s analgesic effect was assessed by the hindpaw thermal withdrawal latency at 60 min after co-administration (10 mg/kg melatonin and/or 10 mg/kg morphine) from day 1 to 14 (A), as well as MPAE% of morphine at 60 min after administration of morphine (20 mg/kg) alone on day 15 (B). A: Injection of morphine (10 mg/kg) significantly increased the thermal withdrawal latency in rats receiving administration of morphine on day 1. However, such an analgesic effect gradually decreased and then disappeared (tolerance) from day 3 to 14 after repeated treatment of morphine. Co-administration of 10 mg/kg melatonin reversed the analgesic effect of morphine. B: The MPAE% of morphine (20 mg/kg) significantly decreased in rats receiving repeated administration of morphine on day 15. However, the decreased MPAE% owing to morphine tolerance was reversed by consecutive 14 days co-administration of morphine with melatonin. MPAE% = [(test latency - basal latency)/(20–basal latency) × 100% (20 s as the cut-off time). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, as compared with the SAL-SAL group at the same time point; # P <0.05 and ## P < 0.01, as compared with the MOR-SAL group at the same time point. Data are presented as mean ± SD for 6 rats per group.
