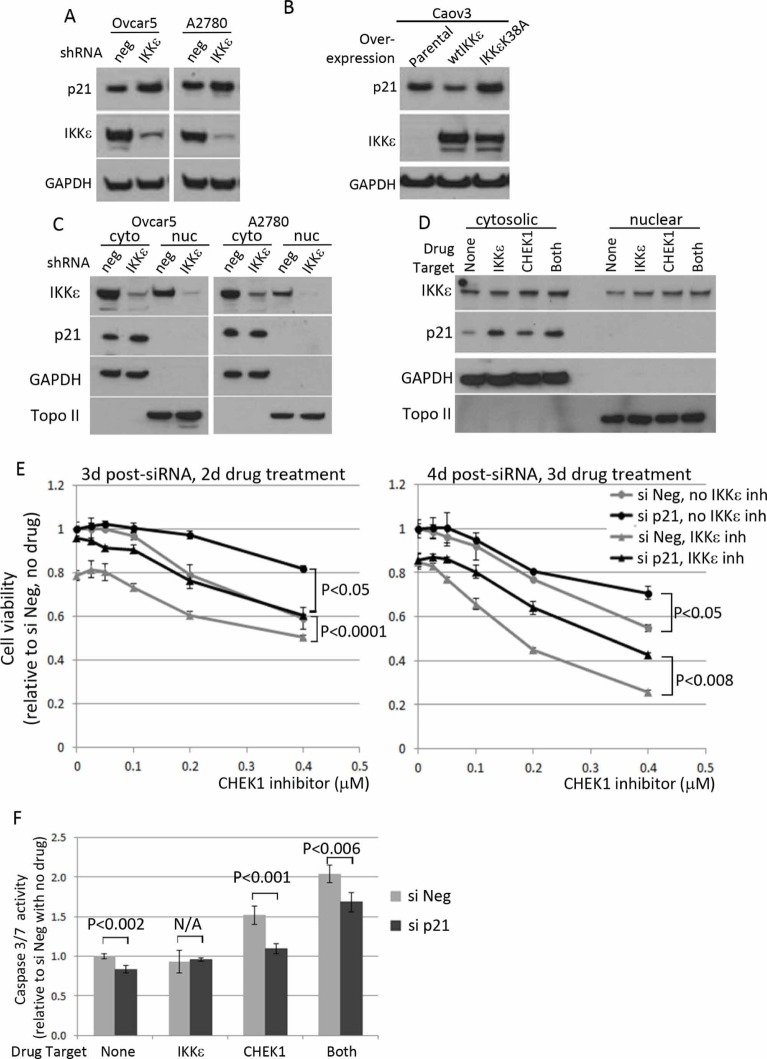
Figure 6. The effect of IKKε manipulation on p21 level and its effect on survival of ovarian cancer cells.
(A) Ovcar5 and A2780 were depleted of IKKε or negative control and maintained under selection (25 μg/ml of mycophenolic acid). Total protein lysates were prepared to examine p21 level and the knockdown of IKKε. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (B) Caov3-wtIKKε and Caov3-IKKε K38A were maintained in selective media (100 μg/ml of G418) and total protein lysates were prepared for the protein analysis. (C) Cytoplasimc and nuclear protein fractionation was prepared using Ovcar5 and A2780 depleted for IKKε (shRNA#1) or control and maintained in culture after magnetic beads purification for LYT2 surface selection marker. (D) Ovcar5 cells were treated for 4 hours with IKKε inhibitor (BX795, 2 μM) and/or CHEK1 inhibitor (PF477736, 0.5 μM) prepared in fresh medium prior to cellular fractionation. GAPDH and Topoisomerase II were used as cytosolic and nuclear markers, respectively. (E) Cells transfected with either siNeg or si p21 were seeded at 2000 cells/well in 50 μl in 3 replicates and 8 hours later PF477736 was added in the absence or presence of BX795 (0.3 μM). XTT assay was performed 2 and 3 days later upon drug treatment. The viability was calculated relative to no drug and siNeg treated samples. The significant p values between siNeg and si p21 samples were calculated by a 2-sided student's t-test. (F) After 16 hours siRNA transfection, cells were seeded and treated for 16 hours with IKKε inhibitor (BX795, 0.3 μM) and/or CHEK1 inhibitor (PF477736, 0.4 μM) in 4 replicates. The caspase3/7 activities were shown relative to untreated siNeg samples from 4 replicates. The significant p values between siNeg and si p21 samples were calculated by a 2-sided student's t-test.