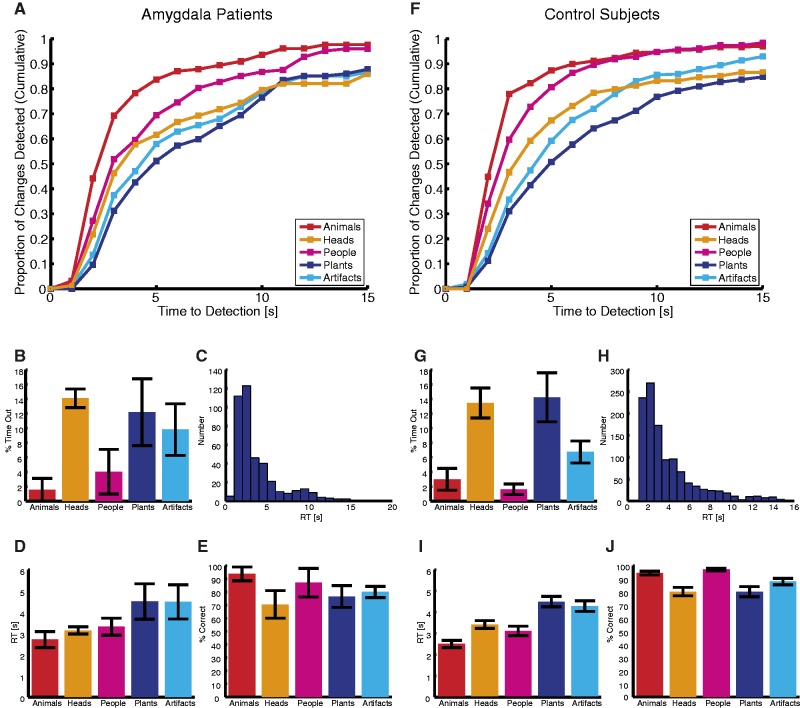
Fig. 2.
Change detection is category-specific. Both amygdala lesion patients (A–E) (N = 4) and control subjects (F–J) (N = 10) showed advantageous change detection of animals, people and head directions over changes to plants and artifacts. (A and F) Graphs show proportion of changes detected as a function of time and semantic category. (B and G) Percentage of time-out for each category. (C and H) RT histogram across all trials. (D and I) Mean RT for each category. (E and J) Percentage of correct detection for each category. Error bars denote one s.e.m. across subjects.