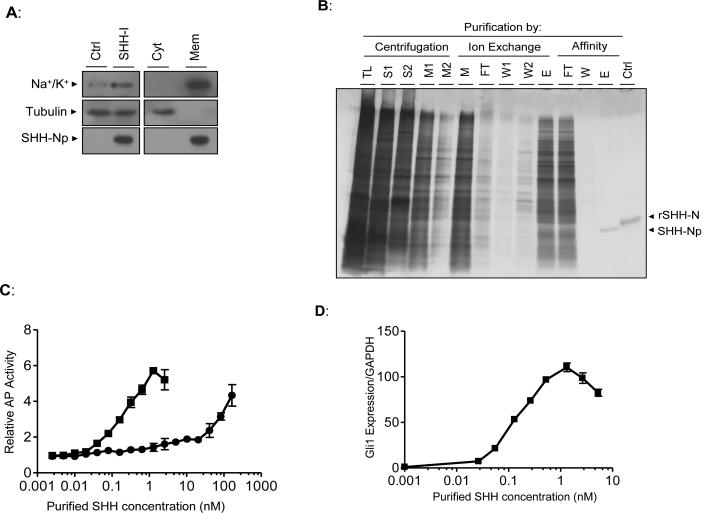
Figure 2. SHH-Np purified from low-level SHH expressing cells is highly active.
(A) SHH-I cells, or the SHH-I parental cell line (Ctrl), were dounce homogenized under isotonic conditions and total lysate (left panel) separated by ultracentrifugation at 100,000 × g (right panel) to generate a cytosol-enriched fraction (Cyt) and a membrane-enriched fraction (Mem). These fractions were volume normalized to that of the original cellular lysate and immunoblotted as indicated. Tubulin serves as a cytosolic protein control while the Na+/K+ transporter serves as a membrane protein control. (B) Aliquots of the indicated fractions from various steps of SHH-Np purification were separated by SDS-PAGE, followed by visualization of proteins by silver staining (TL: total lysate, S: 100,000 × g supernatant, M: combined 100,000 × g pellet detergent extract, FT: non-bound material, W: column wash, E: column eluate). Recombinant, unmodified, SHH-N is shown as a control (rSHH-N). Electrophoretic retardation of rSHH-N, relative to cholesterol modified SHH-Np, has been previously noted (Lee et al., 1994). (C) The indicated amounts of purified SHH-Np were incubated with C3H10T1/2 fibroblasts, which differentiate into osteoblasts in response to SHH (squares: purified SHH-Np, circles: rSHH-N). Alkaline phosphatase activity, which is an indirect, quantitative measurement of this differentiation, was then measured. (D) The indicated amounts of purified SHH-Np were incubated with C3H10T1/2 fibroblasts, followed by RNA extraction. The levels of Gli1 and GAPDH were then determined by q-RT-PCR. Error bars represent the SD in one representative experiment.