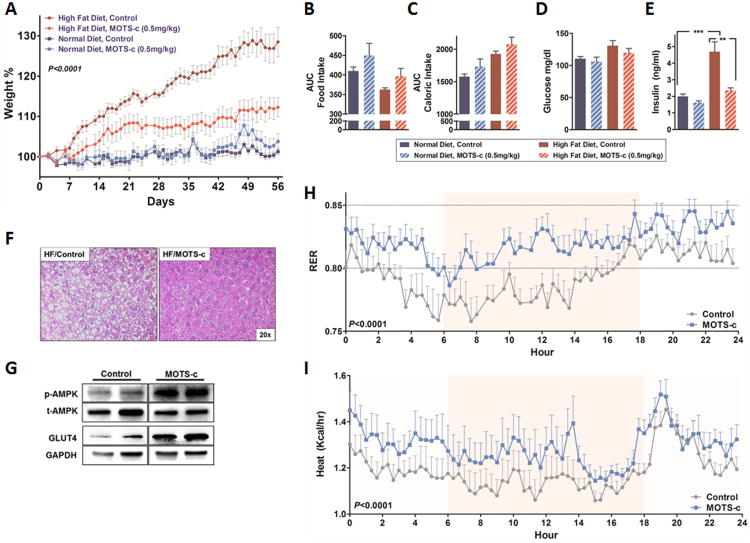
Figure 6. MOTS-c treatment prevents high fat diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance in mice.
8-week old male CD-1 mice fed a high fat diet (HFD, 60% by calories) or matched control diet (N=10) treated with MOTS-c daily (0.5 mg/kg/day; IP) for 8 weeks. (A) body weight, (B) food intake, (C) caloric intake, (D) glucose levels, (E) insulin levels determined at the time of euthanasia, (F) liver H&E staining, and (G) AMPK phosphorylation (Thr172) and GLUT4 levels in the skeletal muscles of HFD-fed mice treated with MOTS-c or vehicle control. (H-I) Respiratory exchange ratio (RER) and body heat production values of 8-week old male CD-1 mice fed a high fat diet (HFD, 60% by calories) or matched control diet treated with MOTS-c daily (0.5 mg/kg/day; IP) for 3 weeks (N=6). Data shown as mean ± SEM. (A, H, and I) Repeated measures two-way ANOVA and (B-E) Student's t-test. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. See also Figure S6 for total activity and Figure S7 for similar data in C57BL/6 mice.