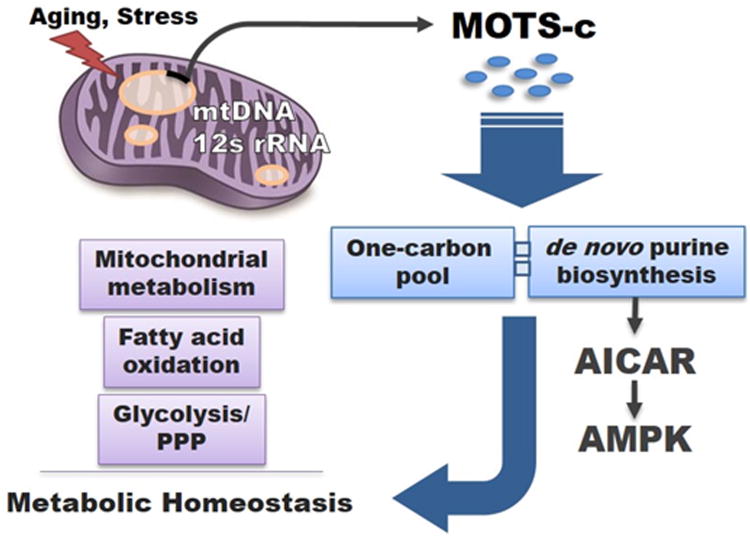
Figure 7. MOTS-c: mitochondrial-encoded regulator of metabolic homeostasis.
Proposed model of MOTS-c as a mitochondrial signaling peptide encoded in the mtDNA that regulates metabolic homeostasis. MOTS-c targets the skeletal muscle and acts on the folate cycle (one carbon pool) and inhibits the directly tethered de novo purine biosynthesis pathway. This leads to the accumulation of the de novo purine synthesis intermediate AICAR that is also a potent activator of the metabolic regulator AMPK, thus partially mediating the metabolic effects of MOTS-c.