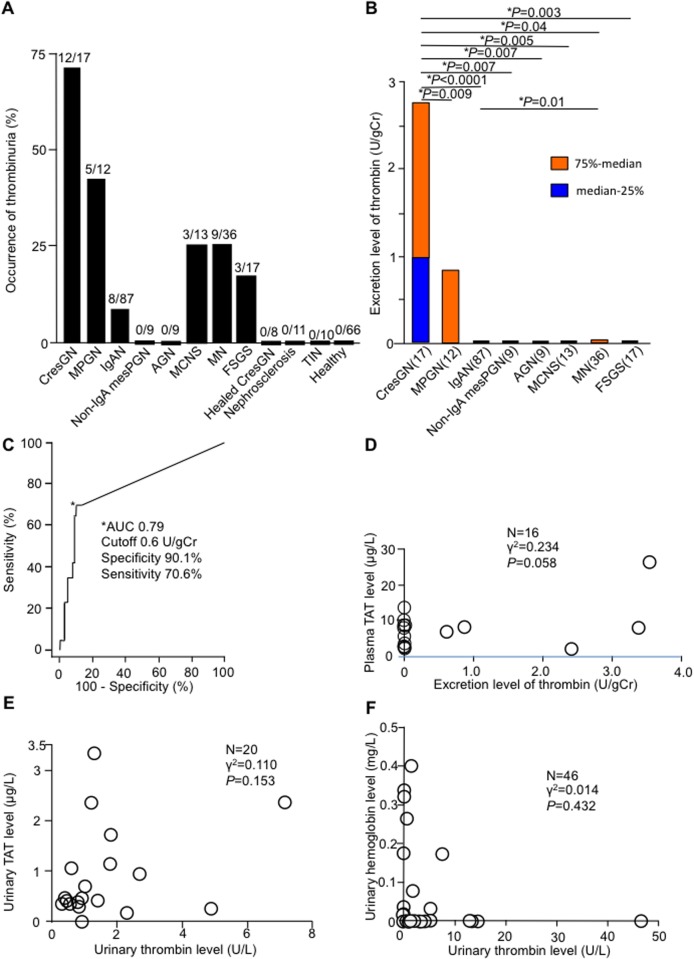
Fig 1. Thrombinuria in glomerulonephritis and its diagnostic accuracy for crescentic glomerulonephritis (CresGN) and its relation to plasma thrombin-antithrombin complex (TAT), urinary TAT, and hemoglobinuria.
(A) Occurrence of urinary thrombin detected (>0.2 U/L) in each group; fractions over the columns indicate the number of samples with thrombin activity per the total number of samples. (B) Thrombin excretion level for each type of glomerulonephritis, as shown by box plots that indicate the median-25th and 75th-median percentiles. Bars with asterisks (*) show only significant differences between two groups. MPGN, membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis; IgAN, IgA nephropathy; non-IgA mesPGN, non-IgA mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis; AGN, acute glomerulonephritis; MCNS, minimal change glomerulopathy; MN, membranous nephropathy; FSGS, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis; and TIN, tubulointerstitial nephritis. gCr indicates gram of urinary creatinine. (C) The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for diagnosis of CresGN in patients with hematuria and proteinuria. The asterisk indicates the diagnostic accuracy at the cutoff value of 0.6 U/gCr. CI indicates confidence interval. (D) Relation of thrombin excretion to plasma TAT. Circles indicate patients with ANCA-associated CresGN (16 measurements in 9 patients). gCr indicates gram of creatinine. (E) Relation of urinary thrombin to urinary TAT. (F) Relation of urinary thrombin to hemoglobinuria. In (E) and (F), each circle represents an individual patient with glomerulonephritis.