Figure 1.
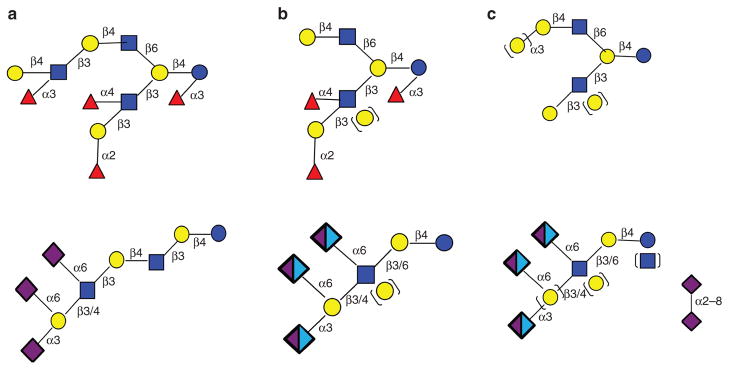
Systematic structural analysis of milk oligosaccharides from multiple mammalian species. Human milk (a) has a higher degree of oligosaccharide polymerization with about 70% fucosylated structures (upper structure) and less than 20% sialylated structures (lower structure, exclusively N-acetylneuraminic acid). Nonhuman primate milk (b) varies with species with 20–65% fucosylated structures (upper structure) and 10–45% sialylated structures (lower structure, both N-acetylneuraminic acid and N-glycolylneuraminic acid). Other mammals (c) show the least degree of polymerization, less than 5% fucosylated structures and up to 70% sialylated structures (lower structure, both N-acetylneuraminic acid and N-glycolylneuraminic acid) (2,79–83). Red triangle = fucose, yellow circle = galactose, blue square = N-acetylglucosamine, blue circle = glucose, purple diamond = N-acetylneuraminic acid, and light blue diamond = N-glycolylneuraminic acid.
