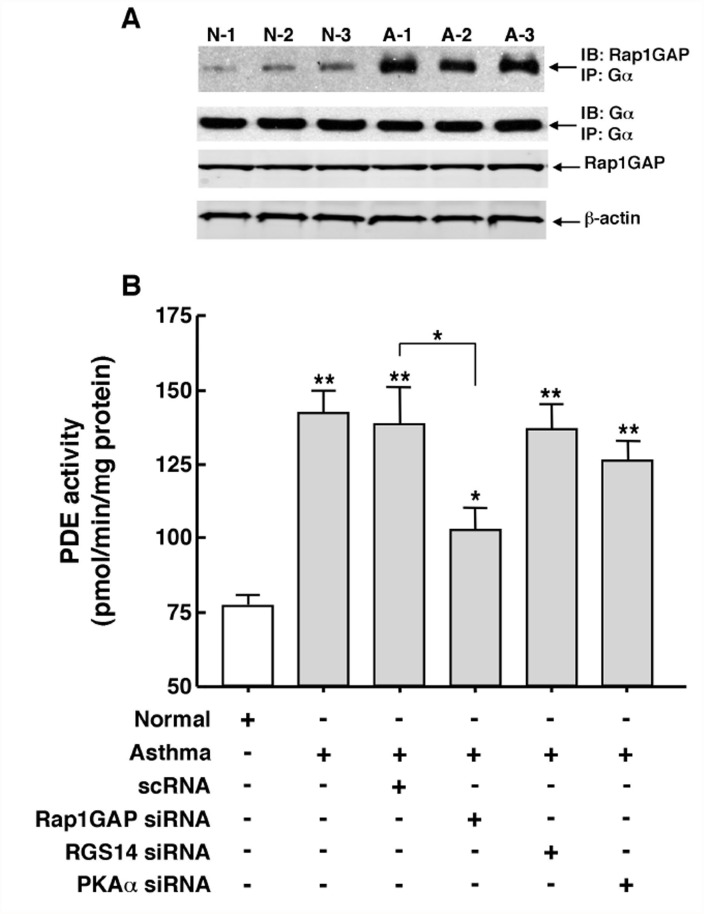
Fig 6. Constitutively increased co-localization of Rap1GAP with Gα protein contributes to upregulated PDE activity in asthmatic HASM cells.
(A) Co-IP analysis demonstrating that, under comparable protein loading given by similar immunoblotted levels of co-immunoprecipitated Gα with anti-Gα immunoprecipitate, relative to 3 normal HASM cell lines, 3 asthmatic HASM cell lines exhibit markedly increased levels of co-immunoprecipitated Rap1GAP. Note: similar conditions of protein loading are also reflected by comparable immunoblotted levels of Rap1GAP, and β-actin. (B) Relative to normal HASM cells, intrinsically heightened PDE activity in asthmatic HASM cells is significantly suppressed by ~40% (p<0.05) in asthmatic cells transfected with a pool of siRNA duplexes targeted against Rap1GAP. By comparison, neither transfection with a scrambled (negative control) siRNA sequence (scRNA) nor pools of siRNA duplexes independently directed against RGS14 and PKAα had a significant effect on PDE activity in asthmatic HASM cells. Data are mean ± SE values, each based on 3–5 determinations. Comparisons between asthmatic vs. normal HASM cells, and between scRNA- vs. Rap1GAP siRNA-transfected asthmatic HASM cells, are made using two-tailed Student t-test. *p<0.05; **p<0.01. Note: neither of the siRNA preparations had a significant effect on PDE activity in normal HASM cells (data not shown).