Figure 3. Different Cul2 and Cul5 interactions with EloC.
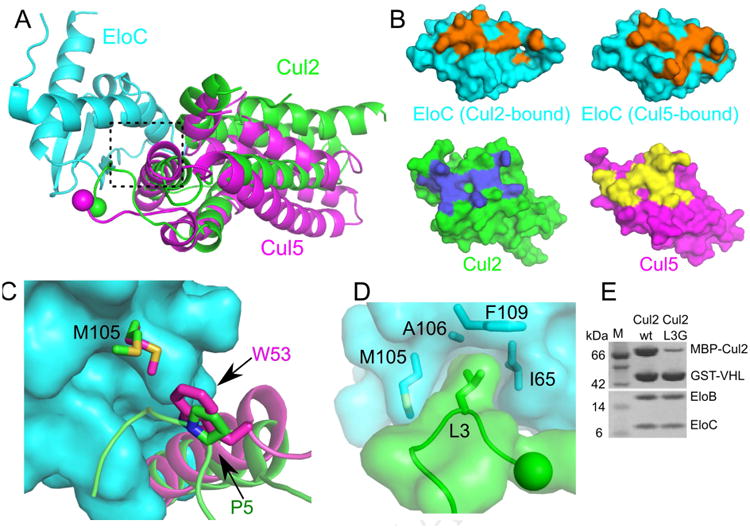
(A) Superposition of the Cul5–EloC (PDB ID: 4JGH) and the current Cul2–EloC structures in ribbon representations. (B) Top, surface representations of EloC bound to either Cul2 (left) or Cul5 (right). Residues involved in the respective cullin interaction are shown in orange. Bottom, surface representations of Cul2 and Cul5 with residues involved in EloC interactions shown in blue and yellow respectively. (C) Differential recognition of EloC M105 by Cul2 (green) and Cul5 (magenta), in the boxed region of A). EloC M105 bound to Cul2 or Cul5 is shown in green or magenta respectively. (D) L3 of Cul2 inserts into a hydrophobic pocket of EloC. The N terminus of Cul2 is shown as a sphere. (E) GST affinity pull-down assay to assess the contribution of Cul2 L3 in binding to VHL–EloBC.
