Figure 4. Interactions between VHL and Cul2.
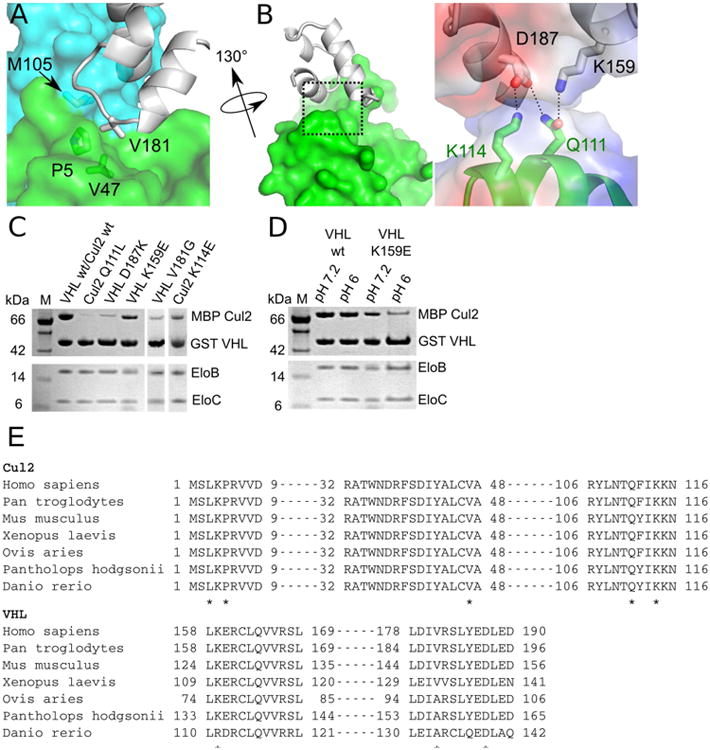
(A) Three-way interaction between the VHL Φp motif, EloC, and helix α2 of Cul2. (B) Left, Binary interaction between VHL and helix α5 of Cul2. Right, Close-up view of the electrostatic network between VHL and Cul2 (boxed region in left). Electrostatic potentials of VHL and Cul2 are shown as semi-transparent surfaces and residues involved are shown as sticks. Dashed lines represent hydrogen bonds or salt bridges. (C) and (D) GST pull-down assays assessing contribution of Cul2 and VHL residues for formation of the quaternary complex. Assays were done at pH 7.2 unless otherwise indicated. (E) Sequence alignments of Cul2 and VHL orthologues. Asterisks denote important residues identified by the structural analysis of the VHL–EloBC–Cul2N quaternary complex.
