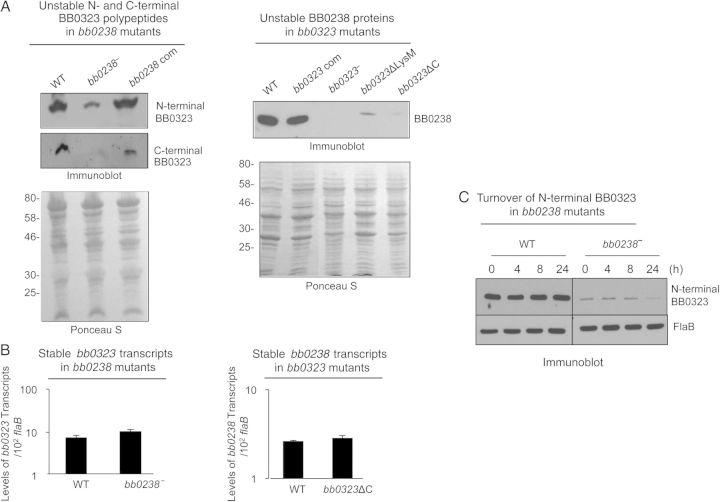
Figure 5.
BB0238 and BB0323 contribute to mutual posttranslational stability. A, Deletion of bb0238 or bb0323 in spirochetes reduces protein levels of the respective partner, as revealed by Western blot analysis. Comparable amounts of lysates from wild-type (WT), bb0238 mutants (bb0238−), bb0238-complemented isolates (bb0238 com), bb0323 mutants (bb0323−), BB0323 C-terminal–deletion mutants (bb0323ΔC), and BB0323 LysM domain–deletion mutants (bb0323ΔLysM) were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and immunoblotted with specific antibodies against BB0238 or N- or C-terminal polypeptides of BB0323. Protein loading is indicated by staining with Ponceau S (bottom panels). Migration of protein standards is shown to the left in kilodaltons (left panel). B, Targeted loss of bb0238 or bb0323 in Borrelia burgdorferi did not alter transcript levels of the respective partner. The level of bb0323 transcripts in WT and bb0238 mutants (top panel) or bb0238 transcripts in WT and bb323 mutants (bb0323ΔC) (bottom panel) was measured with quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. C, Posttranslational stability of BB0323 in bb0238 mutant. Protein synthesis was inhibited by the addition of 100 µg/mL spectinomycin to growing culture of spirochetes, and levels of N-terminal BB0323 were determined with immunoblot analyses. At indicated time points, spirochetes were collected, and lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted using anti-N-terminal BB0323 and anti-FlaB (loading control).