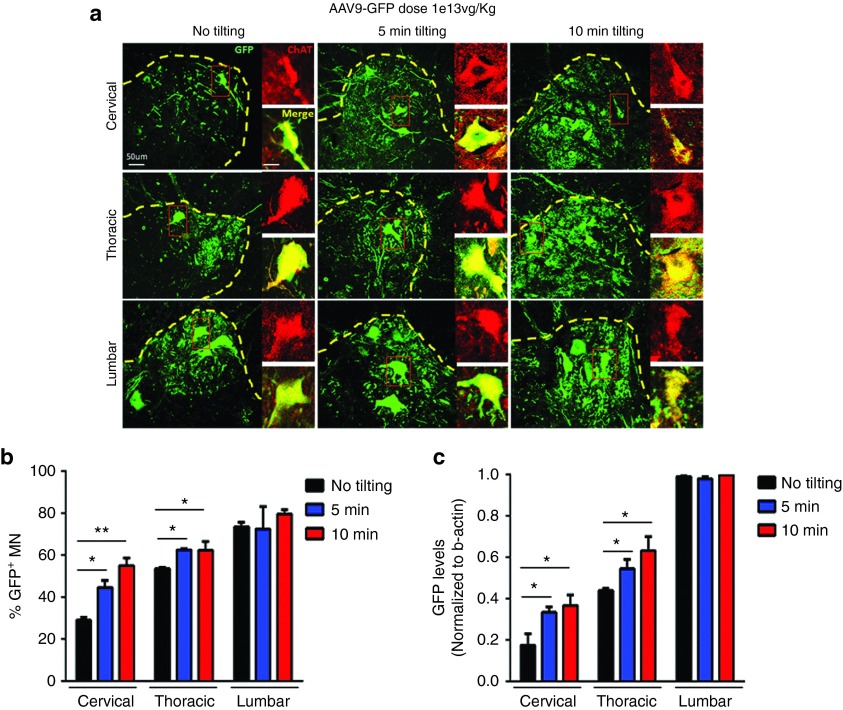
Figure 3.
Single intrathecal sacral injection of 1e13 vg/kg scAAV9.CBA.GFP in nonhuman primates is sufficient to target >50% motor neurons in all spinal cord segments. (a,b) Seven cynomolgus macaques were injected with 1e13 vg/kg scAAV9.CBA.GFP via intrathecal sacral infusion. ChAT/GFP staining and cell counts of double positive cells reveal that keeping the subjects in the Trendelenburg position for 5 (n = 2) or 10 (n = 3) minutes significantly improves motor neuron transduction in both cervical and thoracic spinal cord compared to subjects that received standard procedure (n = 2). This procedure leads to targeting more than 50% motor neurons in all spinal cord segments. (c) GFP mRNA levels correlated with the increase in cell transduction and confirmed the positive effects of adopting the Trendelenburg position to improve virus distribution. Error bars = SD; n = 2–3 per group; *P < 0.05.