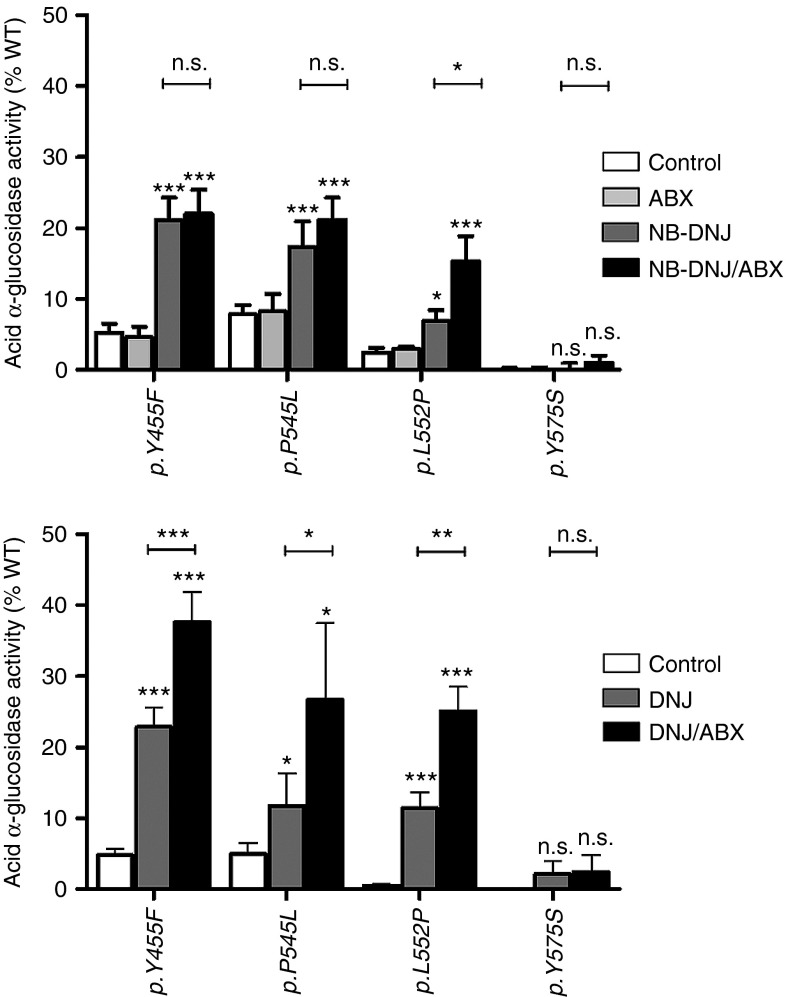
Figure 3.
Acid α-glucosidase (GAA) activity in HEK-293H cells expressing mutant forms of the enzyme treated with a pharmacological chaperone (NB-DNJ or DNJ) and a combination consisting of NB-DNJ/ABX and DNJ/ABX. Upper: PC-responsive mutations of GAA were treated with 40 µmol/l ABX, 20 µmol/l NB-DNJ and a combination of 20 µmol/l NB-DNJ and 40 µmol/l ABX. The monotreatment with ABX did not beneficially influence mutant GAA activity. The NB-DNJ was effective on p.Y455F, p.P545L, and p.L552P, but not p.Y575S. The mutant p.L552P was amenable to the double treatment whereas p.Y455F and p.P545L did not display synergistic effects from the combination of the PC with ABX. Lower: In the same set of mutations, DNJ provoked a similar response compared to NB-DNJ. In combination with ABX, the mutations (except for p.Y575S) showed a siginificant synergistic effect with the imino sugar compared to the monotherapy. Values are shown as mean ± SEM (n ≥ 3). Results were considered significant if *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005.