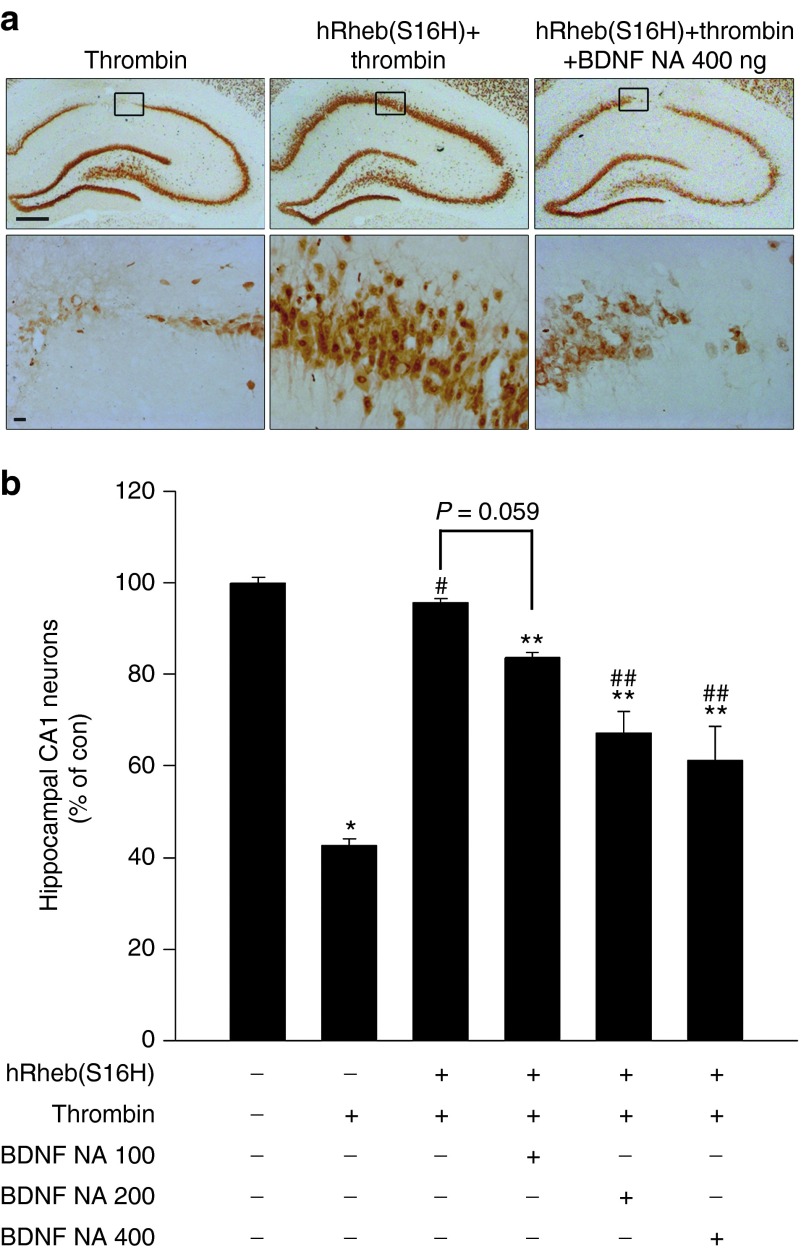
Figure 6.
The induction of BDNF by hRheb(S16H) contributes to the protection of hippocampal neurons. (a) Rats received an intrahippocampal injection of a mixture of BDNF neutralizing antibodies (100, 200 or 400 ng) and thrombin (20 U) at 3 weeks after AAV-hRheb(S16H) injection. Brains were removed and processed for NeuN immunostaining at 1 week following injection of the mixture. As described in Figure 5, hRheb(S16H) protects hippocampal neurons from thrombin-induced neurotoxicity. However, treatment with BDNF neutralizing antibodies attenuates hRheb(S16H)-induced neuroprotection. All pictures show the representative coronal section of each group (n = 5, each group). Bars = 500 and 20 μm, respectively. (b) The number of NeuN-positive hippocampal neurons in the target area of the CA1 layer was expressed quantitatively as a percentage compared to the contralateral control. The results show that hRheb(S16H)-induced BDNF contributes to neuroprotection in the thrombin-treated hippocampus. *P < 0.001, #P < 0.001, **P < 0.05, and ##P < 0.01, significantly different compared with contralateral control side (CON), thrombin alone, CON, and hRheb(S16H)+thrombin, respectively (one-way analysis of variance and Student–Newman–Keulsan analysis; n = 5, each group).