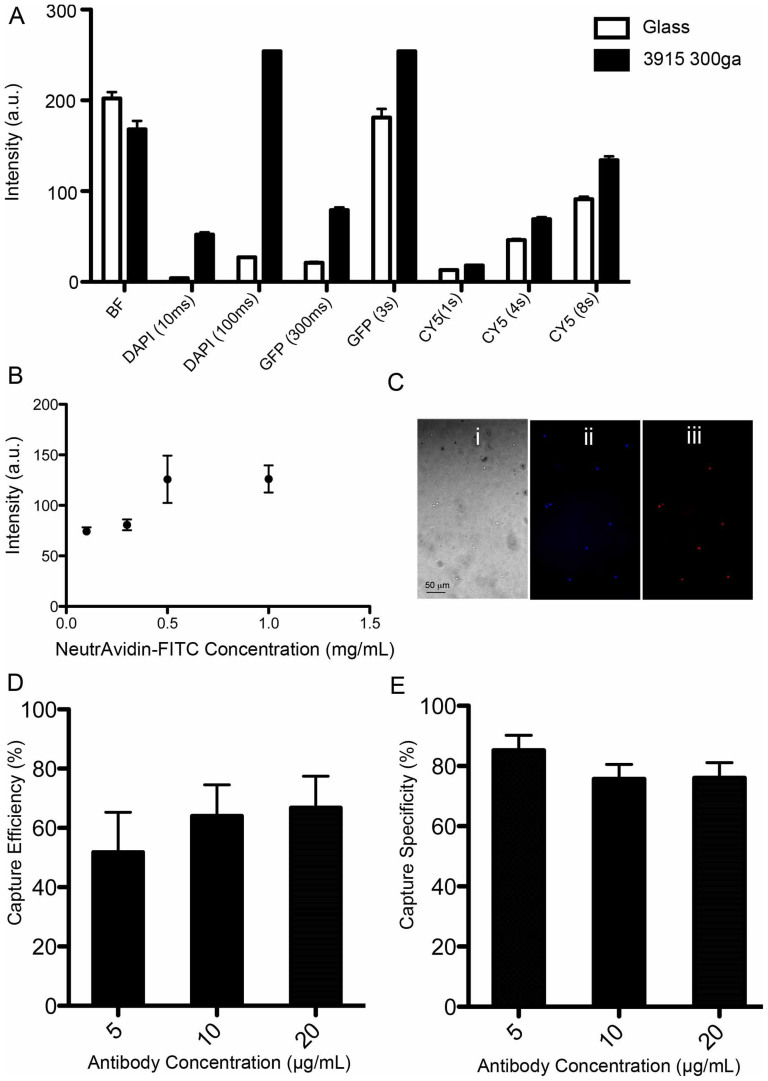
Figure 5. A flexible material (i.e., polyester film)-based platform for the capture of CD4+ T lymphocytes for HIV-1 diagnosis.
In the experiments, glass was determined as a standard substrate, and compared with polyester film (3915 300ga Hostaphan®). (A) Intensity plots for glass and Hostaphan®. Images are taken using various fluorescent filters (DAPI, GFP, and CY5) and exposure time. (B) Fluorescent intensity produced by surface immobilized NeutrAvidin conjugated FITC at various concentrations. (C) Fluorescent images of captured cells on these flexible film-based microfluidic devices. (i) Bright-field image, (ii) DAPI image staining nucleated cells, and (iii) Alexa647 stained CD4+ T lymphocytes cells. (D) Comparison of CD4+ T lymphocytes capture efficiency from whole blood using the platform at various anti-CD4 capture antibody concentrations. There was no statistical difference observed between the groups (n = 3, p > 0.05). (E) Comparison of capture specificity from whole blood using the platform at various anti-CD4 capture antibody concentrations. There was no statistical difference observed between the groups (n = 3, p > 0.05). Statistical assessment was performed using ANOVA with Tukey's posthoc test for multiple comparisons. Statistical significance threshold was set at 0.05 (p < 0.05). Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean.