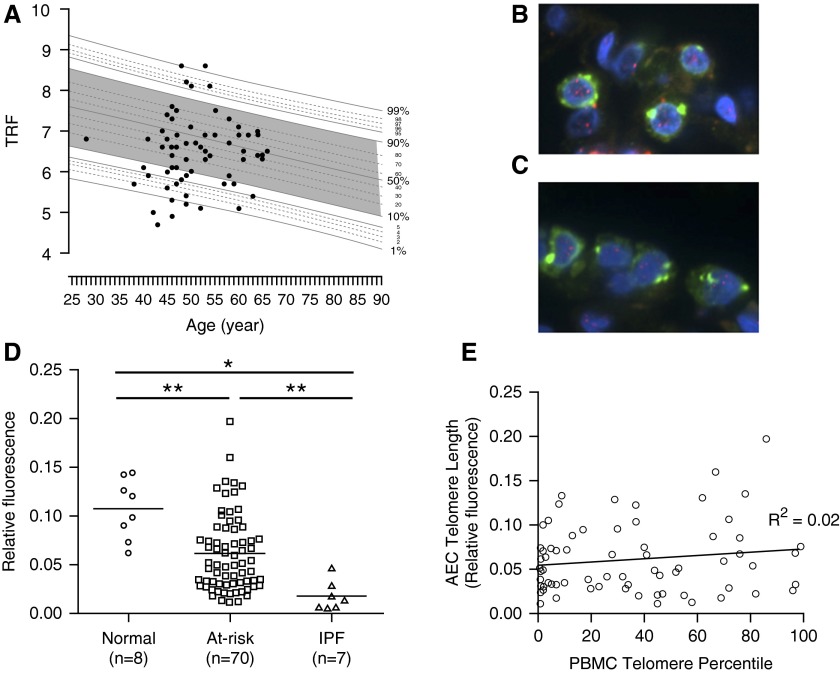
Figure 6.
At-risk subjects have short telomeres in peripheral blood and type II alveolar epithelial cells. (A) DNA was isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of at-risk subjects and telomere restriction fragment (TRF) was measured by Southern blot. TRF was then plotted against age in comparison with a population of normal control subjects. Telomeres less than the 10th percentile for age were considered abnormally short. (B and C) Telomere length in type II alveolar epithelial cells (AECs) was measured using a dual-fluorescence approach wherein type II AECs were identified by costaining for pro–surfactant protein C, and telomeric DNA was quantified relative to total nuclear DNA (DAPI) by relative fluorescence in (B) control and (C) at-risk subjects. Green = pro–surfactant protein C; blue = DAPI (nuclear DNA); red within nucleus = telomeres. (D) Quantification of telomere fluorescence intensity relative to nuclear DNA in type II AECs. *P < 0.001, **P < 0.005. (E) PBMC telomere length was plotted versus AEC telomere length and a linear regression was performed to determine the relationship between PBMC and AEC telomere length. IPF = idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.