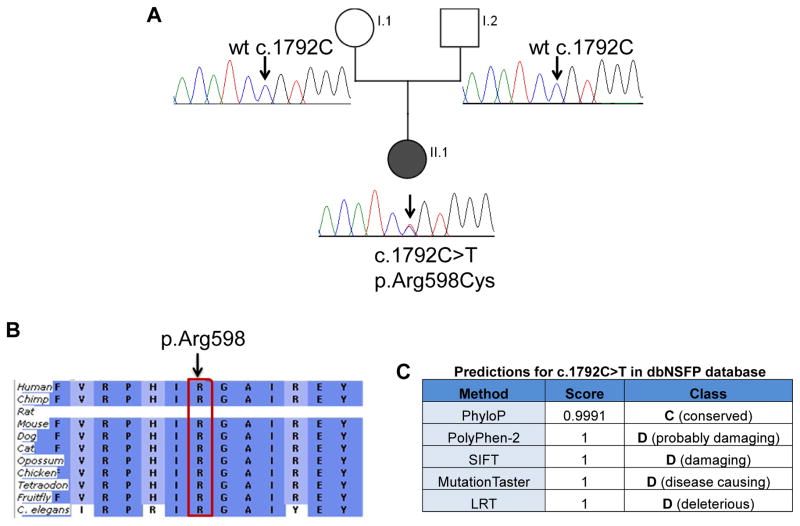
Figure 2.
Detection of mutation in DYNC1H1. Panel A: Sanger sequencing confirmation of novel DYNC1H1 variant (NM_001376.4:c.1792C>T) in proband and parents. Sanger sequencing chromatograms confirm that both unaffected parents have normal alleles at position c.1792 (arrow) and proband is heterozygous at position c.1792C>T causing Arg at position 598 to be changed to Cys. Wt=wildtype. Panel B: Arginine (R) at position 598 in DYNC1H1 is a highly conserved amino acid (generated using Alamut and the Ensembl Compara dataset). Panel C: Pathogenicity prediction for c.1792C>T in dbNSFP (database for nonsynonymous SNPs’ functional predictions) with probability scores ranging from 0 to 1 (0 being benign and 1 being disease causing).