Figure 3. Adoptive transfer of RUPP CD4+ T cells into normal pregnant (NP) rats increases mean arterial pressure (MAP) and circulating CD4+ T cells.
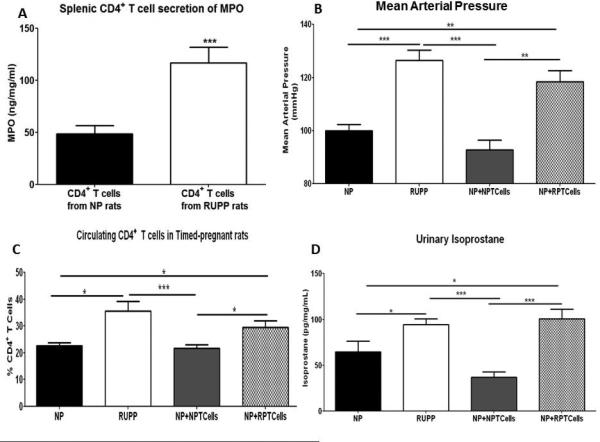
Splenic CD4+ T cells isolated from placental ischemic (RUPP) rats and cultured for 24hrs produced significantly more MPO compared to CD4+ T cells isolated from NP rats (A). MAP was significantly increased in RUPP rats compared to NP rats and to NP+NPCD4+ T cell rats (NP+NPTcells) (B). NP recipients of RUPP CD4+ T cells (NP+RPTcells) had significantly increased circulating CD4+ T cells compared to NP+NP Tcell rats and NP rats. CD4+ T cells are increased in placental ischemic RUPP rats and in NP+RPTcell rats compared to NP rats and NP+NPTcell rats (C). Excretion of urinary isoprostane was significantly increased in RUPP and NP+RPTcell rats compared to NP and NP+NPTcell rats (D). Data is expressed as mean±standard error mean. *p <0.05, **p<0.005, ***p<0.0005 between indicated groups.
