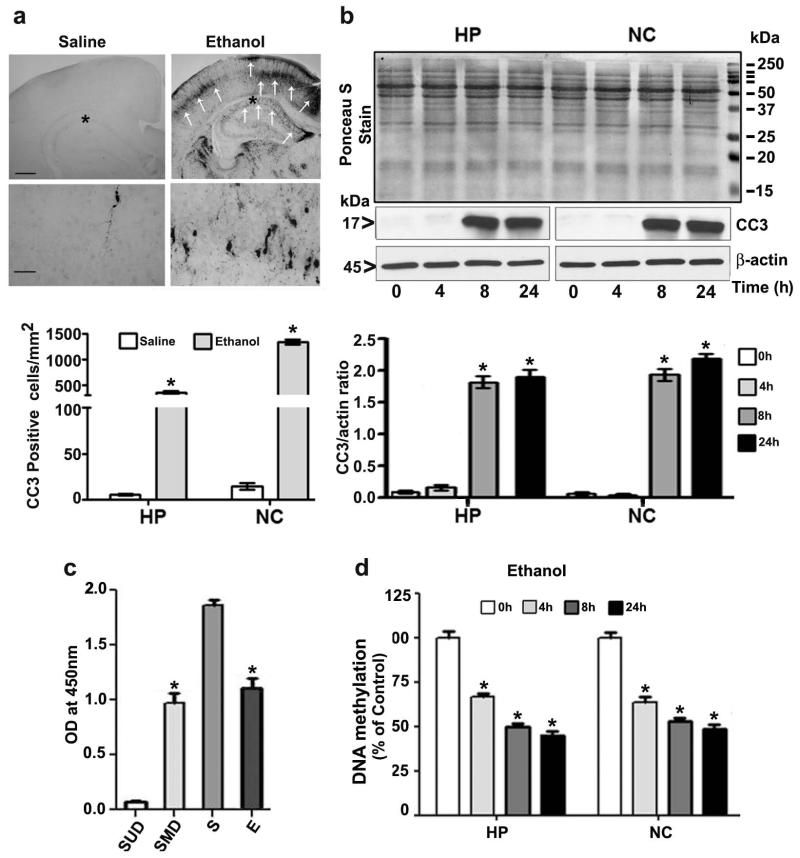
Fig. 1.
Ethanol exposure induces apoptotic neurodegeneration and reduces DNA methylation in the P7 mouse brain. (a) Coronal brain sections (hippocampus and retrosplenial cortex) from saline- and ethanol-treated animals were immunostained with an anti-rabbit CC3 antibody. The white arrows indicate CC3-positive neurons in the hippocampus and retrosplenial cortex, respectively. Scale bars = 200 μm. The respective images were enlarged to show CC3-positive cells (*). The scale bars represent 50 μm. CC3-positive cells were counted in the hippocampus and the retrosplenial cortex (n =10 pups/group). (b) Western blot analysis of CC3 using cytosolic extracts (20 μg) of hippocampal and neocortical samples obtained 4–24 h after the first saline or ethanol injection (n = 15 pups/group). Ponceau S staining confirmed equal loading and β-actin were used as loading controls. *p < 0.05 vs. 0 h or saline control (One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test). For 0 h ethanol group, saline was injected. (c) Global DNA methylation assay specificity was determined using synthetic unmethylated DNA (contains 50% of cytosine) (negative control) (SUD) and methylated DNA (contains 50% of 5-methylcytosine) (positive control) (SMD). The OD was used with the kit’s included formulas to calculate the global DNA methylation levels. S, saline; E, ethanol. (d) Global DNA methylation quantification in hippocampal (HP) and neocortical (NC) DNA obtained 4–24 h after the first saline or ethanol injection. For 0 h ethanol group, saline was injected. Error bars, SEM. Error bars, SEM. HP, hippocampus; NC, neocortex. (*p < 0.05, n = 10 pups/group) (One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test).