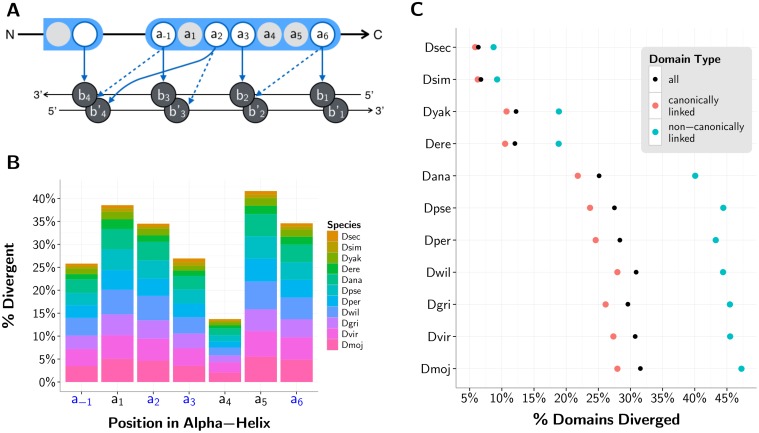
Fig 3. C2H2-ZF domain divergence with respect to D. melanogaster reference.
(A) Schematic of a C2H2-ZF protein—DNA interface under the 7-contact model [53]. Amino acids within the depicted finger are numbered according to their relative position from the start of the alpha helix within the C2H2-ZF domain, with a-1 indicating the position before the start of the helix. Bases b1, b2, b3 and b4 are numbered sequentially from 5’ to 3’ of the primary DNA strand; the complementary bases are denoted by b1’, b2’, b3’ and b4’. Contacts between amino acids and bases are shown in arrows, with four specificity-determining amino acids a-1, a2, a3 and a6 making these contacts. Solid arrows depict the four “canonical” contacts between ZF domains and DNA [52], and dashed arrows depict three additional contacts that are used in our predictions of binding specificity [53]. (B) Histogram showing the percent divergence per species by position within the C2H2-ZF domain’s alpha-helix (-1 to 6) for all canonically linked domains. The columns with blue labels in the x-axis correspond to positions that interact with DNA in the 7-contact model. (C) Percent of all (black), canonically linked (blue) and non-canonically linked (red) aligned domains in each non-reference fly species with a divergent residue (as compared to the D. melanogaster reference) in positions -1, 2, 3, and/or 6.