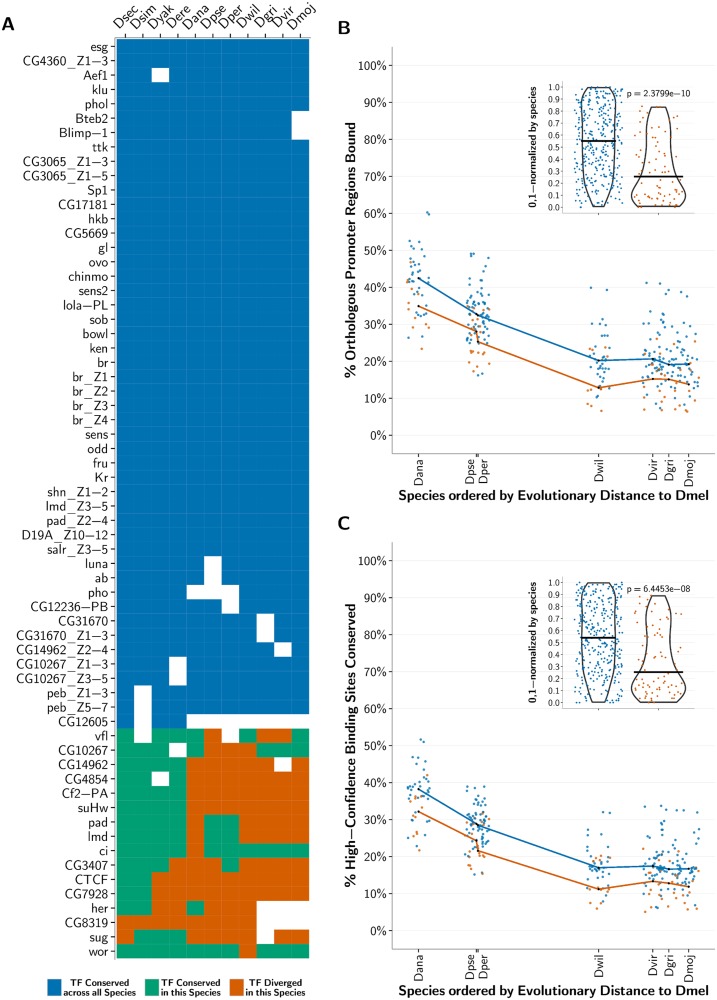
Fig 6. Conservation of predicted binding motifs for experimentally derived PWMs across species.
(A) The list of analyzed experimentally determined C2H2-ZF binding specificity motifs (PWMs) within D. melanogaster along with a heat map representing the conservation of the corresponding protein construct across the fly species; note that each PWM was determined either for an entire protein or just a fragment of it. In the heat map, white depicts that a 1-to-1 ortholog for the corresponding C2H2-ZF protein in D. melanogaster was not present in that species; blue depicts that the DNA-contacting residues within the C2H2-ZF construct are conserved across all the flies; green depicts that the DNA-contacting residues within the C2H2-ZF construct did not diverge in that species, but one or more of these residues diverged in one or more orthologs in the other fly species; and orange depicts that the C2H2-ZF in the current species diverged from its 1-to-1 ortholog in D. melanogaster in at least one DNA-contacting residue within the protein construct. (B) For each species, ordered on the x-axis by its relative evolutionary distance from D. melanogaster, we plot for each PWM in panel A the fraction of promoters predicted to be bound in D. melanogaster whose orthologous regions within the species are also predicted to be bound. Blue points correspond to C2H2-ZFs conserved across all the flies, and orange points correspond to C2H2-ZFs that diverge in the current species. The medians of the conserved and diverged C2H2-ZFs for each species are computed and plotted as black points. Lines connecting these median points are drawn for visual effect only. For each species, conserved C2H2-ZF proteins tend to bind a higher proportion of promoter regions that are orthologous to those bound in D. melanogaster than do diverged C2H2-ZF proteins. (Part B Inset) Violin plots showing the per-species 0, 1-normalized ranks of percent orthologous promoter regions bound, such that the rank of the lowest percentage per species maps to 0, and the rank of the highest percentage maps to 1. The p-value comparing the normalized percentages between conserved and diverged C2H2-ZF orthologs is calculated using a Wilcoxon test. (C) Same as part B, where y-axis values correspond to the percent of high-confidence D. melanogaster binding sites conserved in each species for each PWM. For each species, conserved C2H2-ZF proteins tend to have a higher fraction of binding sites conserved from D. melanogaster than do diverged C2H2-ZF proteins.