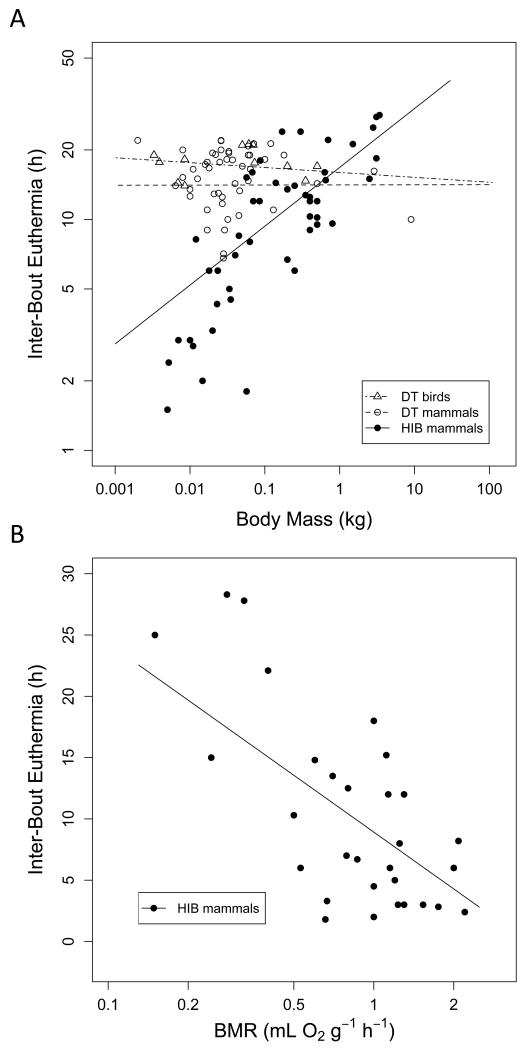
Fig. 10.
A) Duration of inter-bout euthermia as a function of body mass. There was no significant relationship to body mass in avian (t=−0.59, P=0.562) or mammalian (t=0.01, P=0.987) daily heterotherms, but the duration of euthermia episodes increased with body mass among mammalian hibernators (log10IBE=1.22+0.255 log10BM, t=4.59, P<0.0001, R2=0.66). B) The relationship between basal metabolic rate (BMR) and the duration of interbout euthermia in mammalian hibernators (IBE=8.92-15.39 log10BMR, t=−3.80, P<0.001, R2=0.50). There was no such relationship in daily heterotherms (data not shown for clarity).