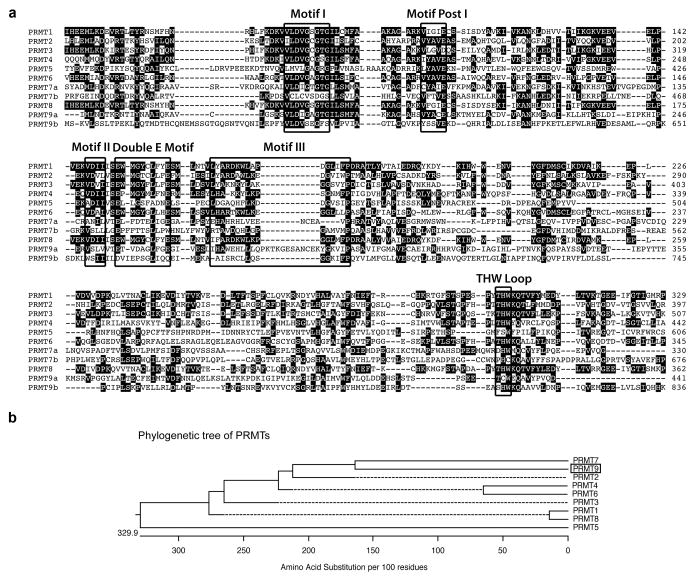
Fig. 1. Amino acid sequence alignment of human PRMTs.
(a) The amino acid sequences from the catalytic domain of PRMTs are compared using ClustalW. The signature sequence motifs are boxed with black squares, including the motifs common to seven beta strand enzymes (Motif I, Motif Post I, Motif II, and Motif III) as well as the Double E Motif and THW Loop motifs that are specific to PRMTs. The number on the right indicates the positions of amino acid of individual PRMT, starting at the initiator methionine. Human PRMT sequences used included PRMT1: NP_001527.3; PRMT2: NP_996845.1; PRMT3: NP_005779.1; PRMT4: NP_954592.1; PRMT5: NP_006100.2; PRMT6: NP_060607.2; PRMT7: NP_061896.1; PRMT8: NP_062828.3; and PRMT9: NP_612373.2.
(b) A straight branches phylogenetic tree of all human PRMTs (shown in phenogram) was generated using ClustalW to demonstrate the evolutionary relationships among these enzymes. Protein sequence accession numbers used in the analysis are listed above.