Fig 1. DNA cleavage and type I topoisomerase mechanisms.
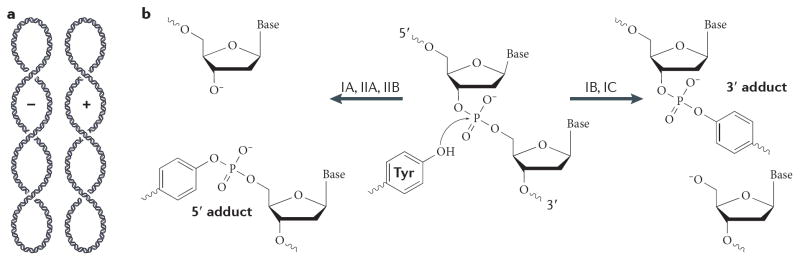
(A) Schematic of negative (−) and positive (+) plectonemic DNA supercoiling. The two forms can be distinguished by their right- and left-handed superhelical wrapping, respectively. (B) Schematic of the DNA cleavage reaction. Topoisomerases catalyze strand scission by forming a reversible, covalent enzyme–DNA adduct through their active site tyrosine. Type IB and IC topoisomerases become attached to 3′ DNA ends, and type IA and II topoisomerases attach to 5′ DNA ends. (C) Type IA topoisomerases pass a single-stranded DNA segment (yellow) through a transient break in a second, single DNA strand (green). The structure of E. coli topo III (a type IA topoisomerase) bound to single-stranded DNA is shown 210. (D) Type IB topoisomerases nick one DNA strand (yellow), allowing one duplex end (green strand) to rotate with respect to the other around the remaining phosphodiester bond. The structure of human topo IB bound to duplex DNA is shown 20.
