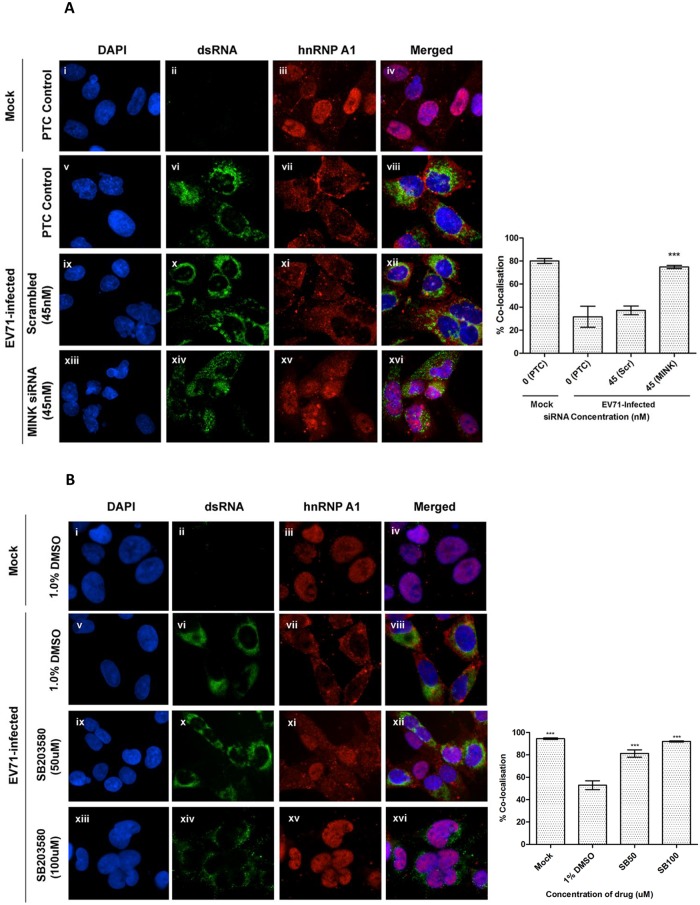
Fig 8. MINK silencing and p38 MAPK inhibition in EV71-infected cells inhibits cytoplasmic localisation of hnRNP A1.
(A) RD cells were pre-treated with MINK targeting and scrambled siRNA and subjected to infection with EV71. siRNA-treated cells were fixed and the subcellular localisation of hnRNP A1 (red), an IRES-transacting factor, was investigated by indirect immunofluorescence assay. Immunofluorescence detection of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA, green) with the nuclei stained with DAPI (blue) was shown to indicate EV71 infection. The images were taken at 100X magnification. Colocalisation quantification was based on the Manders Overlap Coefficient (MOC) using whole-cell immunofluorescence (WCIF) ImageJ software [36] and represented as percent colocalisation at the respective siRNA concentrations. Error bars represent the standard deviation of duplicate data. (B) RD cells were subjected to infection with EV71 and post-treated with SB203580 (p38 MAPK inhibitor) for 8h. SB203580-treated cells were fixed and the subcellular localisation of hnRNP A1 (red) was investigated by indirect immunofluorescence assay. Mock-infected and DMSO-treated cells were included as infection and solvent control, respectively. The images were taken at 100X magnification. Colocalisation quantification was based on the MOC using WCIF ImageJ software and represented as percent colocalisation at the respective drug concentrations. Error bars represent the standard deviation of duplicate data.