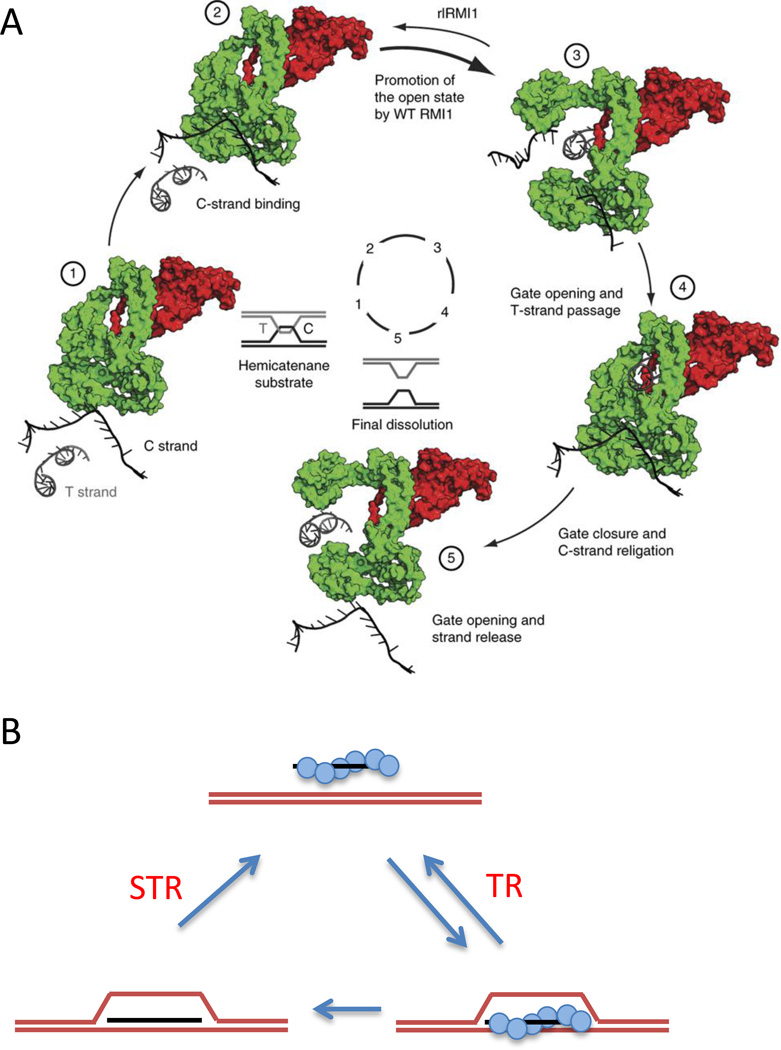
Figure 2.
Roles of STR and TR in reversing the formation of D-loops. A. Mechanism of strand passage carried out by mammalian TOPIIIα-RMI1 as illustrated by (Bocquet et al., 2014). TopIIIα cleaves the C strand and undergoes a conformational change that allows the transfer strand (T) to pass through, after which the C strand is re-ligated and the gate closes, with release of the C strand. This action is stimulated by a loop of RMI1 that is part of the active site. Figure reused with permission from Bocquet et al., NSMB 2014 Figure 5. B. Rad51 (blue circles) coating single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) facilitates strand invasion and the formation of a D-loop in the presence of the ssDNA binding protein complex, RPA, and Rad54. When the D-loop is protein-free, Sgs1 alone, or STR, can take apart the D-loop, but Sgs1 alone cannot dismantle the protein-bound. This protein-bound form can be taken apart by the Top3-Rmi1 complex acting alone.