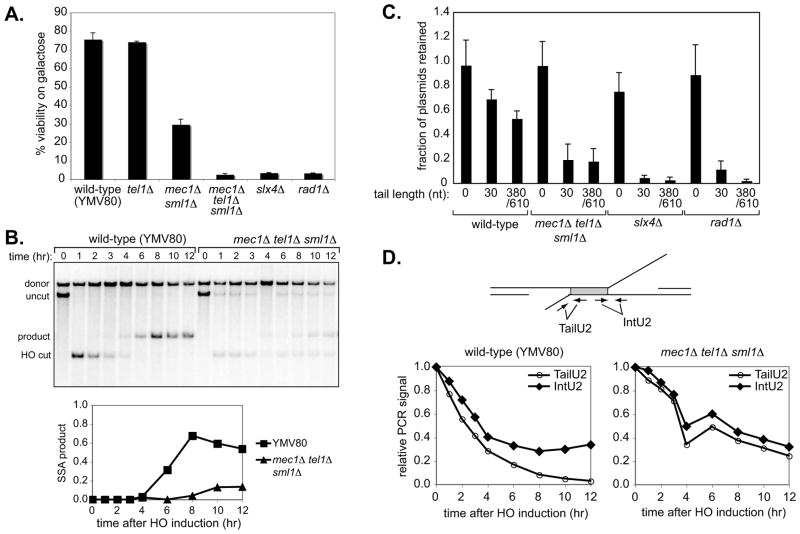
Figure 4. Mec1/Tel1 are required for 3′ non–homologous tail removal during HR.
(a) The efficiency of SSA repair in wild-type (YMV80) or mec1Δ sml1Δ (YMV126), tel1Δ (GTY36), mec1Δ tel1Δ sml1Δ (GTY35), slx4Δ (GTY11) and rad1Δ (GTY32) strains was determined by plating on glucose or galactose media, as described in Materials and Methods. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM) from three separate experiments. (b) Upper panel: Southern blot analysis of SSA in wild-type (YMV80) and mec1Δ tel1Δ sml1Δ (GTY35) strains. Lower panel: quantitation of SSA product formation in YMV80 and GTY35. (c) Gene conversion efficiency was measured in wild-type (YMN4), mec1Δ tel1Δ sml1Δ (YFD814), slx4Δ (tNS2362) and rad1Δ (tNS2372) strains containing hmlΔmatα-inc hmrΔ and transformed with the plasmids pFP122, pFP140 or pFP120. Mean fractions of plasmids retained ± 95% confidence interval (CI) are shown. (d) 3′ non-homologous tail formation and removal was assayed in wild-type (YMV80) and mec1Δ tel1Δ sml1Δ (GTY35) strains by qPCR, using primer pairs TailU2 and IntU2 to detect the non-homologous tail and internal control (repeat) regions as indicated.