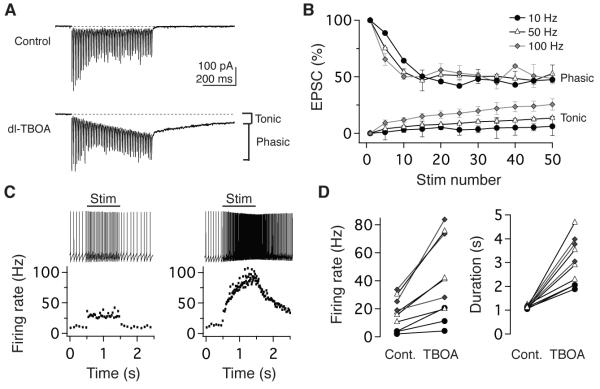
Figure 6.
The temporal fidelity of postsynaptic responses requires active glutamate uptake. (A) Example EPSCs evoked by 100 Hz stimulation in ACSF (top) and following the addition of the 200 μM dl-TBOA (bottom), which resulted in the accumulation of a tonic current in addition to phasic EPSC responses. (B) In dl- TBOA, phasic EPSC responses remained rate-invariant in response to train stimulation at 10, 50, and 100 Hz, however the tonic current progressively increased with rate (n=4). EPSCs normalized to EPSC1 peak amplitude. (C) Example evoked postsynaptic firing responses to a 1-s, 50-Hz train (left) and following dl-TBOA application (right). The instantaneous firing rate (below) demonstrates a step-like response under control conditions and an enhanced, long-lasting response in dl- TBOA. (D) The population effects of blocking glutamate transporters on the firing rate (left) and duration (right) of postsynaptic responses to 1-s stimuli.