Figure 1.
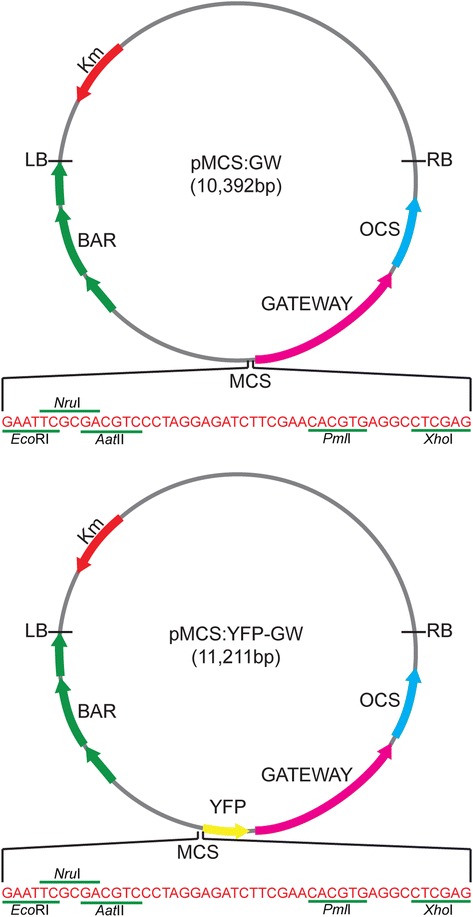
pMCS:YFP-GW and pMCS:GW plant transformation vectors. pMCS:YFP-GW and pMCS:GW were derived from the pEarleyGate104 [12] and pEarleyGate100 [12] vectors, respectively. The pMCS:YFP-GW and pMCS:GW vectors are binary vectors for plant transformation and confer kanamycin (Km, red arrow) and chloramphenicol (in Gateway cassette) resistance in Escherichia coli and kanamycin resistance (Km, red arrow) in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plants transformed with these vectors will display resistance to phosphinothricin (Basta; BAR consisting of the basta resistance gene driven by the mannopine synthase promoter and flanked by the mannopine synthase 3′ end; three green arrows). The multiple cloning site (MCS) allows for cloning of desired promoters for expression of downstream genes transferred into the vector using Gateway technology. The Gateway cassette (attR1, chloramphenicol resistance gene, ccdB, attR2; pink arrow) is followed by the terminator sequence from the octopine synthase gene (OCS, blue arrow). In addition, pMCS:YFP-GW has the yellow fluorescence protein (YFP, yellow arrow) gene downstram of the MCS and in-frame with the Gateway cassette. The left border (LB) and right border (RB) of the T-DNA are marked.
