Figure 4.
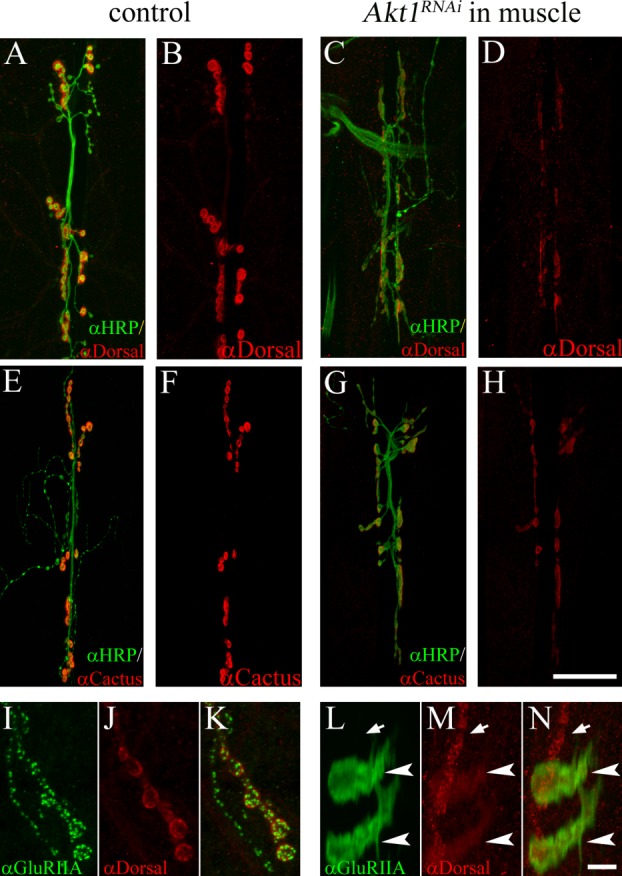
Influence of Akt1 on Dorsal and Cactus levels and distribution at the NMJ. A and B: In control animals (UAS-Akt1RNAi/+), Dorsal (detected by anti-Dorsal antibody; red) is localized to the postsynaptic specialization. Neuronal projections were labeled by anti-HRP staining (green). C and D: Akt1 function was compromised by expressing UAS-Akt1RNAi under the muscle-specific 24B-GAL4. Dorsal levels at the NMJ were significantly reduced. E and F: Cactus (red) was concentrated at the NMJ in control animals. G and H: Inhibition of Akt1 function in the muscle (24B-GAL4/UAS-Akt1RNAi) resulted in reduced levels of Cactus at the NMJ. I–K: In control animals, Dorsal immunoreactivity (red) colocalized with GluRIIA (green) immunoreactivity at the postsynaptic specialization. L–N: In muscles where Akt1 expression was inhibited, both Dorsal and GluRIIA redistributed into intracellular bands, although the effect on Dorsal was less and incompletely penetrant. Mislocalized Dorsal partially overlapped with GluRIIA (arrowheads indicate bands of Dorsal and GluRIIA; arrows indicate synaptic boutons). Scale bar in (A–H), 50 µm, in (I–N), 5 µm.
